Automate Connection Management With Python
Use Case
You want to get started writing programmatic scripts in Python that interact with the Fivetran REST API. A common use case for this is to automate processes around creating, updating, or running connections on a custom schedule. You are looking for an example of how to get started.
Recommendation
Fivetran recommends starting off with simple examples to familiarize yourself with how to interact with our API using Python.
Create a connection with Python - example
The following code example walks you through the process of creating a connection using the REST API.
Code example
# =========================================
# Fivetran connector creation automation script
# -----------------------------------------
# This script demonstrates how to automate the creation of Fivetran connectors using the Fivetran REST API.
# It is designed for users who want to programmatically deploy multiple connectors (for example, for different schemas).
#
# Tips:
# - You can adapt this script to create, update, or delete connectors by changing the HTTP method and payload.
# - Store your API credentials securely (never hardcode in production).
# - Use configuration files or environment variables for sensitive data.
# - Review Fivetran API docs for more endpoints and options: https://fivetran.com/docs/rest-api
# =========================================
import requests
from requests.auth import HTTPBasicAuth
import json
import colorama
from colorama import Fore, Back, Style
# -----------------------------------------
# CONFIGURATION
# -----------------------------------------
# TIP: Store your API key/secret and other parameters in a config file or environment variables for security.
r = 'config.json'
with open(r, "r") as i:
l = i.read()
y = json.loads(l)
api_key = y['API_KEY']
api_secret = y['API_SECRET']
a = HTTPBasicAuth(api_key, api_secret)
a = HTTPBasicAuth(api_key, api_secret)
# -----------------------------------------
# API REQUEST
# -----------------------------------------
# This function wraps the Fivetran API call logic for reusability.
# You can use it for GET, POST, PATCH, DELETE requests by changing the method argument.
def atlas(method, endpoint, payload):
base_url = 'https://api.fivetran.com/v1'
h = {
'Authorization': f'Bearer {api_key}:{api_secret}'
}
url = f'{base_url}/{endpoint}'
try:
if method == 'GET':
response = requests.get(url, headers=h, auth=a)
elif method == 'POST':
response = requests.post(url, headers=h, json=payload, auth=a)
elif method == 'PATCH':
response = requests.patch(url, headers=h, json=payload, auth=a)
elif method == 'DELETE':
response = requests.delete(url, headers=h, auth=a)
else:
raise ValueError('Invalid request method.')
response.raise_for_status() # Raise exception for 4xx or 5xx responses
return response.json()
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
print(f'Request failed: {e}')
return None
# -----------------------------------------
# MAIN LOGIC
# -----------------------------------------
# TIP: Adapt the following section to your use case.
# - 'p' is the source authentication (for example, password)
# - 'destination' is the Fivetran group ID where connectors will be created
# - 'new_schema' is a list of schema prefixes for each connector
# - You can add more fields to the payload as needed (see Fivetran docs https://fivetran.com/docs/rest-api)
# Example: Load parameters from config
p = y['T'] # source auth (for example, password)
destination = y['D'] # destination group ID
new_schema = ["s_011", "s_012","s_013"] # List of schema prefixes for new connectors
method = 'POST' # Use 'POST' to create, 'PATCH' to update, 'GET' to retrieve, 'DELETE' to remove
endpoint = 'connectors/'
# Loop through each schema and create a connector
for schema_prefix in new_schema:
payload = {
"service": "sql_server_rds", # TIP: Change this to your desired Fivetran connector type
"group_id": destination, # The group (destination) where the connector will be created
"trust_certificates": "true",
"run_setup_tests": "true",
"paused": "true",
"pause_after_trial": "true",
"config": {
"schema_prefix": schema_prefix, # Each connector gets a unique schema prefix
"host": "", # DB host
"port": 1433, # Default SQL Server port; change if needed
"database": "sqlserver", # DB name
"user": "fivetran", # DB user
"password": p # Use the password loaded above
}
}
# Submit the connector creation request
print(Fore.CYAN + "Submitting Connector")
response = atlas(method, endpoint, payload)
# Review the response and print results
if response is not None:
print('Call: ' + method + ' ' + endpoint + ' ' + str(payload))
print(response['code'] + ' ' + response['message'])
print(Fore.MAGENTA + "Connector: " + response['data']['id'] + " successfully created in " + str(destination))
# =========================================
Best practices and suggestions
- Clone the repository for the Fivetran API framework, which contains the above Connection Creation using Fivetran REST API example
- To automate at scale, consider reading connector configs from a .CSV file or database. See the example that implements reading schema names from a CSV file
- Use version control for your automation scripts
- Always test with a single connection before running bulk operations
- Review Fivetran REST API rate limits and error codes for robust automation
- Review the Fivetran API documentation for more endpoints and options
- For more advanced automation, integrate with CI/CD pipelines or orchestration tools.
Sync an existing connection with Python - example
The following code example walks you through the process of manually syncing an existing connection in a group using the API. The diagram below illustrates the process.
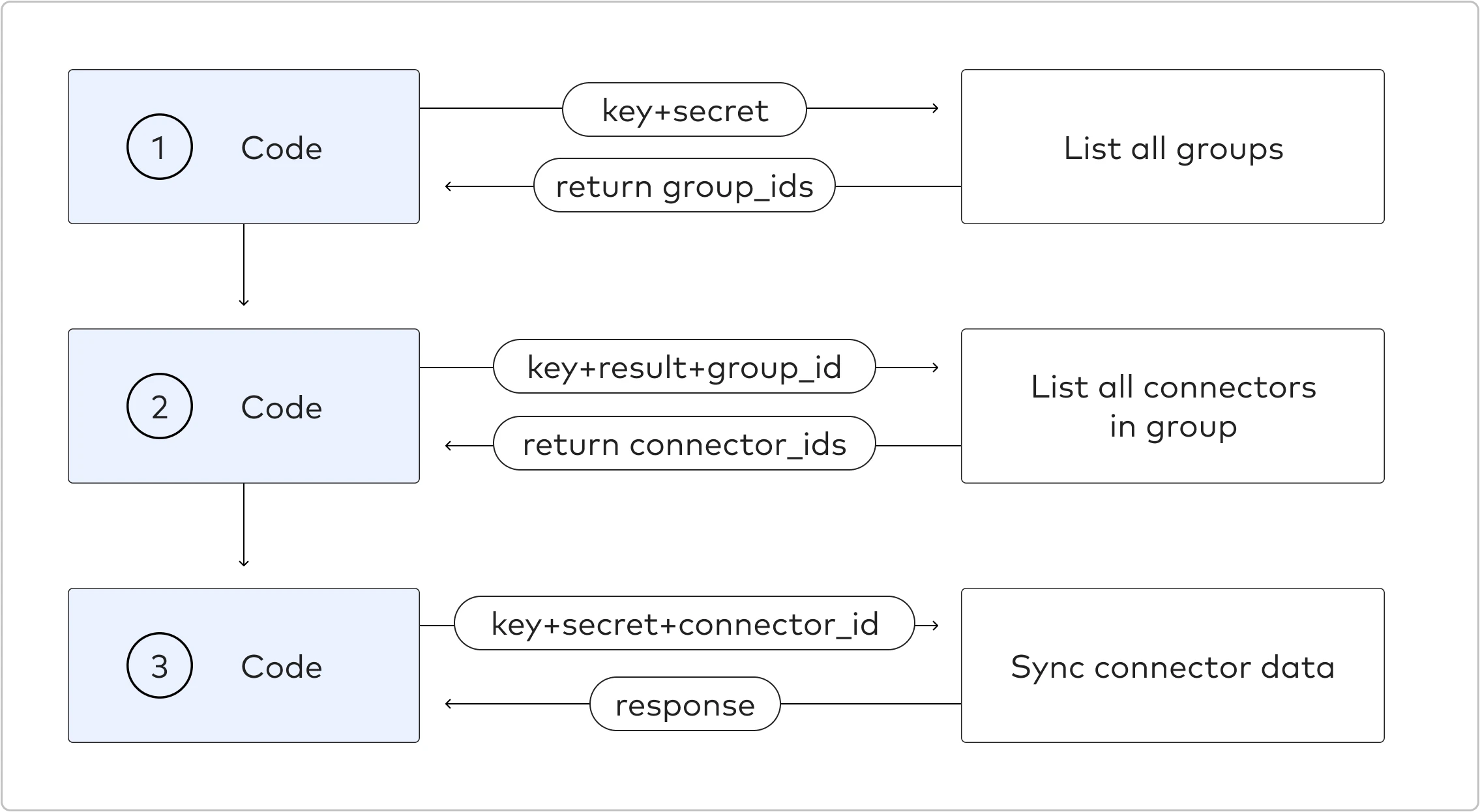
Code example
import requests
from requests.auth import HTTPBasicAuth
import json
import colorama
from colorama import Fore, Back, Style
def atlas(config_path):
# Load configuration
with open(config_path, "r") as i:
config = json.load(i)
api_key = config['fivetran']['api_key']
api_secret = config['fivetran']['api_secret']
auth = HTTPBasicAuth(api_key, api_secret)
base_url = 'https://api.fivetran.com/v1'
headers = {
'Authorization': f'Bearer {api_key}:{api_secret}'
}
def make_request(method, endpoint, payload=None):
url = f'{base_url}/{endpoint}'
try:
if method == 'GET':
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers, auth=auth)
elif method == 'POST':
response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, json=payload, auth=auth)
else:
raise ValueError('Invalid request method.')
response.raise_for_status()
return response.json()
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
print(f'Request failed: {e}')
return None
# Get groups
groups = make_request('GET', 'groups')
#print(groups)
if groups is None or not groups['data']['items']:
print(Fore.RED + "No groups found or unable to fetch groups.")
return
# Get the last group
last_group = groups['data']['items'][-1]
last_group_id = last_group['id']
print(Fore.BLUE + f"Selected last group: {last_group['name']} (ID: {last_group_id})")
# Get connections for the last group.
# connections = make_request('GET', f'groups/{last_group_id}/connections')
# Or, a specific group
group_id = ''
connections = make_request('GET', f'groups/{group_id}/connections')
#print(connections)
if connections is None or not connections['data']['items']:
print(Fore.RED + f"No connections found in group {group_id} or unable to fetch connections.")
return
# Get the last connection
last_connection = connections['data']['items'][-1]
last_connection_id = last_connection['id']
print(Fore.BLUE + f"Selected last connection: {last_connection['schema']} (ID: {last_connection_id})")
# Trigger sync for the last connection
sync_result = make_request('POST', f'connections/{last_connection_id}/sync')
if sync_result is not None:
print(Fore.GREEN + f"Sync triggered for connection {last_connection_id} in group {last_group_id}")
print(Fore.CYAN + f"Response: {sync_result['message']}")
else:
print(Fore.RED + f"Failed to trigger sync for connection {last_connection_id}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
config_path = '/config.json'
atlas(config_path)