Amazon RDS for MariaDB Setup Guide
Follow these instructions to replicate your Amazon RDS for MariaDB database to your destination using Fivetran.
Prerequisites
To connect your Amazon RDS for MariaDB database to Fivetran, you need:
MariaDB 10.1.2 - 11.7
MariaDB versions earlier than 10.1.2 may function correctly, with the exception of fractional seconds in the TIME, TIMESTAMP, and DATETIME columns. Before version 10.1.2, fractional seconds were stored differently, which caused problems with our incremental updates.
Your database host's IP (for example,
1.2.3.4) or domain (your.server.com)Your database's port (usually
3306)A unique replica ID for Fivetran. We need this ID because we connect to your database as a replica. We provide a random replica ID in your setup form, but you can provide your own if you'd prefer or if the form's replica ID conflicts with one of your existing replica IDs.
The replica ID is a unique ID within the MariaDB replica set.
(If you're using TLS) Your server must support at least TLSv1.0, but we recommend TLSv1.2 or above
For IAM-based authentication, IAM authentication must be enabled on your Amazon RDS for MariaDB instance. For instructions, see Enabling IAM Database Authentication.
Setup instructions
Do not perform the Choose connection method step if you want to use Hybrid Deployment for your data pipeline.
Choose connection method
First, decide whether to connect Fivetran to your Amazon RDS for MariaDB primary database or read replica directly, using an SSH tunnel, using AWS PrivateLink, or using Proxy Agent. How you configure your security groups in later steps will differ depending on this decision.
Connect directly (TLS required)
You must have TLS enabled on your database to connect directly to Fivetran. Follow Amazon's TLS setup instructions to enable TLS on your database.
Fivetran connects directly to your Amazon RDS for MariaDB database. This is the simplest method.
If you connect directly, you will create a rule in a security group that allows Fivetran access to your database instance.
Connect using SSH (TLS optional)
Fivetran connects to a separate server in your network that provides an SSH tunnel to your database. You must connect through SSH if your database is in an inaccessible subnet.
If you connect using SSH, you will configure your tunnel server's security group to allow Fivetran access and configure your database's security to allow access from the tunnel.
Before you proceed to the next step, you must follow our SSH connection instructions. If you want Fivetran to tunnel SSH over TLS, follow Amazon's TLS setup instructions to enable TLS on your database.
Connect using AWS PrivateLink
You must have a Business Critical plan to use AWS PrivateLink.
AWS PrivateLink allows VPCs and AWS-hosted or on-premises services to communicate with one another without exposing traffic to the public internet. PrivateLink is the most secure connection method. Learn more in AWS’ PrivateLink documentation.
Follow our AWS PrivateLink setup guide to configure PrivateLink for your database.
Connect using Proxy Agent
Fivetran connects to your database through the Proxy Agent, providing secure communication between Fivetran processes and your database host. The Proxy Agent is installed in your network and creates an outbound network connection to the Fivetran-managed SaaS.
To learn more about the Proxy Agent, how to install it, and how to configure it, see our Proxy Agent documentation.
Authenticate using IAM (optional)
Fivetran supports AWS IAM database authentication as an alternative to a password-based login. IAM authentication offers enhanced security and centralized access control.
- IAM authentication must be enabled on your Amazon RDS for MariaDB instance.
- IAM authentication is not available for connections using AWS PrivateLink.
You can use IAM database authentication when your connection runs in either SaaS Deployment or Hybrid Deployment mode.
Expand for SaaS Deployment instructions
Retrieve external ID
Open your Fivetran connection setup form.
In the Authentication Method drop-down menu, select IAM.
Copy the External ID shown in the form. You will need it when creating an IAM role in AWS.
The External ID is unique to your Fivetran account but remains the same even if you close and reopen the form.
Create IAM policy for Fivetran
In your AWS IAM console, go to Access management > Policies, then click Create policy.
In the Create policy window, switch to the JSON tab and paste the following policy:
{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "rds-db:connect" ], "Resource": [ "arn:aws:rds-db:{region}:{account-id}:dbuser:{DbiResourceId}/{db-user-name}" ] } ] }Replace the placeholders:
{region} – your DB instance’s AWS region (for example,
us-east-1){account-id} – your AWS account number
{DbiResourceId} – your RDS instance’s Resource ID (You can find it in the AWS RDS console under Configuration for the DB instance.)
{db-user-name} – the name of the database user for authentication using IAM. You can choose any name now; you will create the user during the Create user and configure incremental updates step.
Click Next: Review Policy.
Name the policy (for example,
Fivetran-RDS-Access).Click Create policy.
Create IAM role for Fivetran
In your AWS IAM console, go to Access management > Roles, then click Create role.
In the Create role window, select AWS Account as the trusted entity type.
Select Another AWS account, then in the Account ID field, enter Fivetran's AWS account ID:
834469178297.In Options, select the Require external ID checkbox.
Enter the External ID you found in your connection setup form.
Click Next: Permissions.
Select the policy that you created earlier (for example,
Fivetran-RDS-Access).Click Next: Review.
Name the role (for example,
Fivetran), then click Create role.Select the Fivetran role you've just created.
Find the Role ARN and make a note of it. You will need it to configure Fivetran.
Expand for Hybrid Deployment instructions
Create IAM policy for Fivetran
In your AWS IAM console, go to Access management > Policies, then click Create policy.
In the Create policy window, switch to the JSON tab and paste the following policy:
{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "rds-db:connect" ], "Resource": [ "arn:aws:rds-db:{region}:{account-id}:dbuser:{DbiResourceId}/{db-user-name}" ] } ] }Replace the placeholders:
{region} – your DB instance’s AWS region (for example,
us-east-1){account-id} – your AWS account number
{DbiResourceId} – your RDS instance’s Resource ID (You can find it in the AWS RDS console under Configuration for the DB instance.)
{db-user-name} – the name of the database user for authentication using IAM. You can choose any name now; you will create the user during Step 6.
Click Next: Review Policy.
Name the policy (for example,
Fivetran-RDS-Access).Click Create policy.
Create IAM role and attach it to container host
These instructions assume that your Hybrid Deployment Agent container runs on an Amazon EC2 instance or in Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS), in the same AWS account as your Amazon RDS instance.
Use the IAM policy you created earlier (Fivetran-RDS-Access) and assign it to the appropriate environment:
- For EC2: Follow the instructions in How to Use an IAM Role Assigned to an EC2 Instance in AWS with Hybrid Deployment, skipping the Create IAM Policy step since you have already created the required IAM policy (Fivetran-RDS-Access).
- For EKS: Follow the instructions in How to Use an IAM Role Assigned to a Kubernetes Service Account in AWS with Hybrid Deployment, skipping the Create IAM Policy step since you have already created the required IAM policy (Fivetran-RDS-Access).
Choose incremental sync method
To keep your data up to date after the initial sync, we use one of the following incremental sync methods:
- Binary log
- Fivetran Teleport Sync
Fivetran Teleport Sync disables large, rapidly changing tables if they fail to sync. Learn more in the Teleport general limitations documentation.
Each of these methods keeps a record of recent data changes, which allows Fivetran to update only the data that has changed since our last sync.
To learn the differences between the two methods, see our incremental sync documentation.
Create read replica (optional)
If you'd like, create a read replica for Fivetran's exclusive use. Using a read replica also allows us to integrate your data without putting unnecessary load on or interrupting the queries running on your primary server. We recommend that you connect a read replica to Fivetran, but it's not required.
If you want to connect Fivetran to your primary database or already have a read replica, skip ahead to Step 5.
Expand for instructions
In your Amazon RDS dashboard, select the MariaDB primary instance that you want to replicate.
Click Actions, then select Create Read Replica.
In the Settings section, enter your chosen instance ID.
In the DB instance size section, specify the instance class for the read replica. It does not need to be as large as your primary instance.
In the Connectivity section, set the Public access setting to Publicly accessible to ensure that the read replica is accessible from outside your VPC.
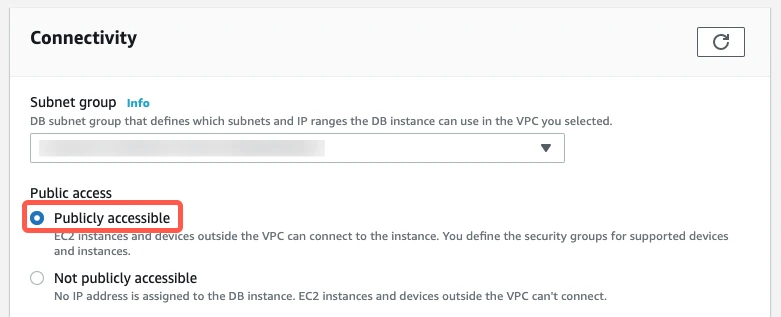
Click Create read replica.
The replica's status should now be
creating. It will take a few minutes for the read replica to finish being created. The status will change toavailablewhen it is done.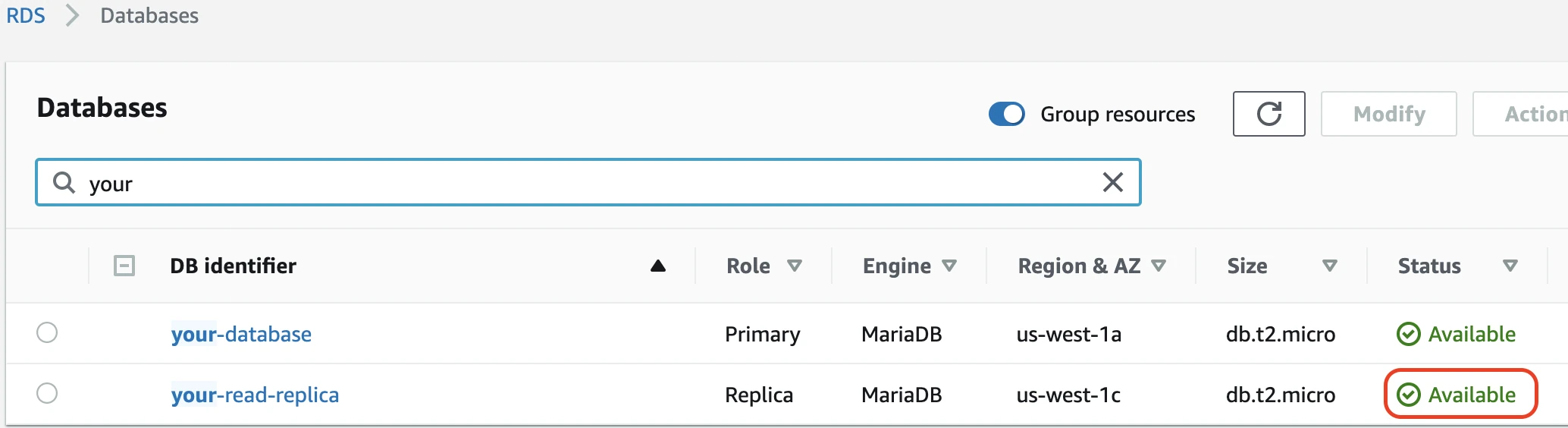
Enable database access
Grant Fivetran's data processing servers access to your database server. How you grant access depends on whether or not your database instance is in a VPC.
If your instance is in a VPC, you must configure the two methods that control access: VPC security groups and network access control lists (ACLs). If your instance is not in a VPC, you only need to configure security groups.
Configure security group
Expand for instructions
These instructions assume that your database instance is in a VPC. If your database instance is not in a VPC, you can still use these instructions because configuring a non-VPC security group is an almost identical process.
In your Amazon RDS dashboard, click on the database that you want to connect to Fivetran.
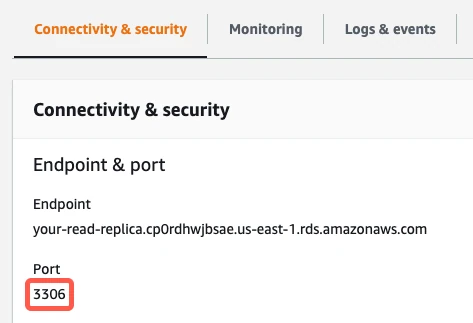
In the Endpoint & port column, find the database's port number and make a note of it. You will need the port number to configure Fivetran.
In the Security column, click the link to the database instance's security group.
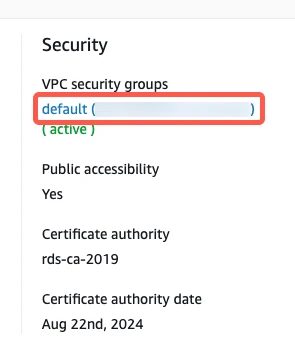
In the Security Group panel, click Actions, then select Edit inbound rules from the drop-down menu.
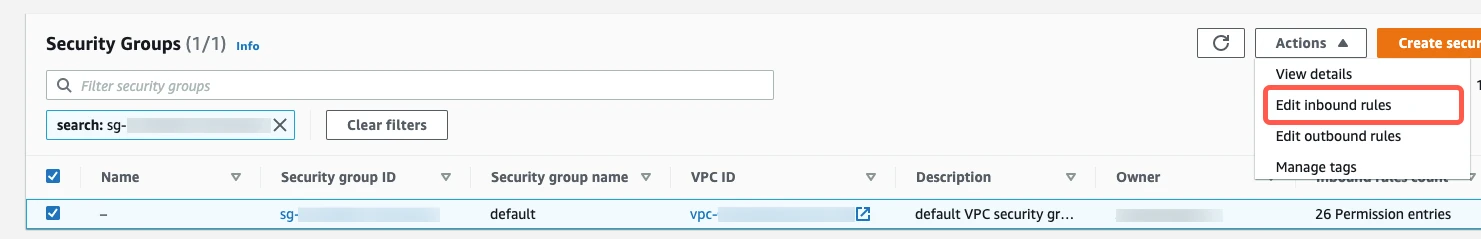
Click Add Rule. This creates a new Custom TCP Rule at the bottom of the list with a blank space for a Port Range and a Source IP address.
Fill in the new Custom TCP Rule.
- In the Port Range field, enter your database's port number that you wrote down in Step 2 of this section. The port number will be
3306for direct connections, unless you changed the default. - What you enter in the Custom IP field depends on whether you're connecting directly or using an SSH tunnel.
- If you're connecting directly, enter Fivetran's IPs for your database's region.
- If you're connecting using an SSH tunnel, enter
{your-ssh-tunnel-server-ip-address}/32.
- (Optional) Enter a brief description in the Description field.
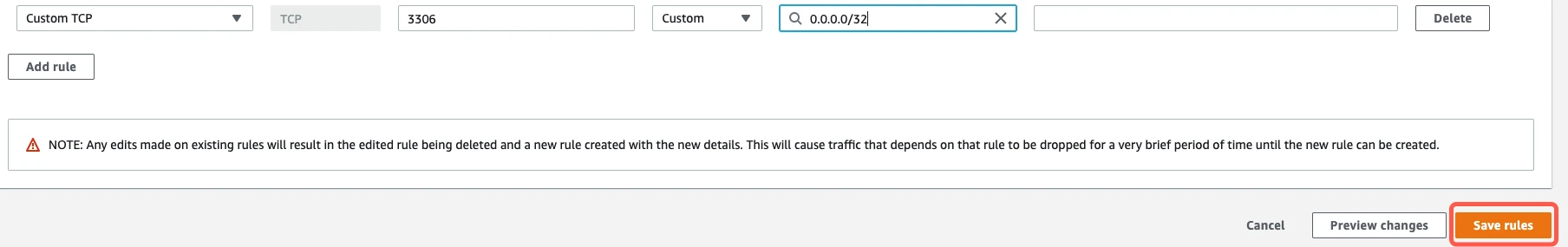
- In the Port Range field, enter your database's port number that you wrote down in Step 2 of this section. The port number will be
Click Save rules.
Configure Network ACLs (VPC only)
Expand for instructions
If your database instance is not in a VPC, skip ahead to Step 6.
Return to the RDS Dashboard.
Click on your MariaDB database.

In the Networking column, click the link to the instance's VPC.
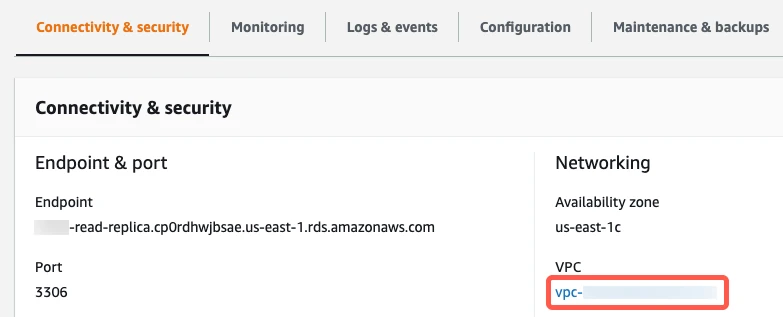
Select the VPC.
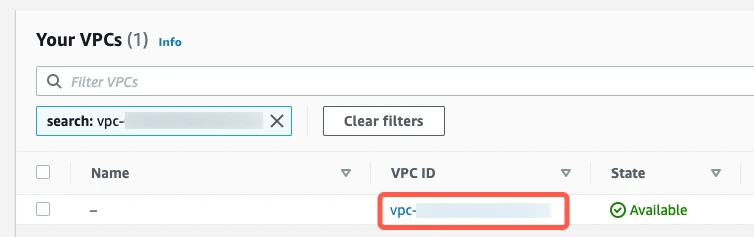
In the Summary tab, click the Network ACL link.
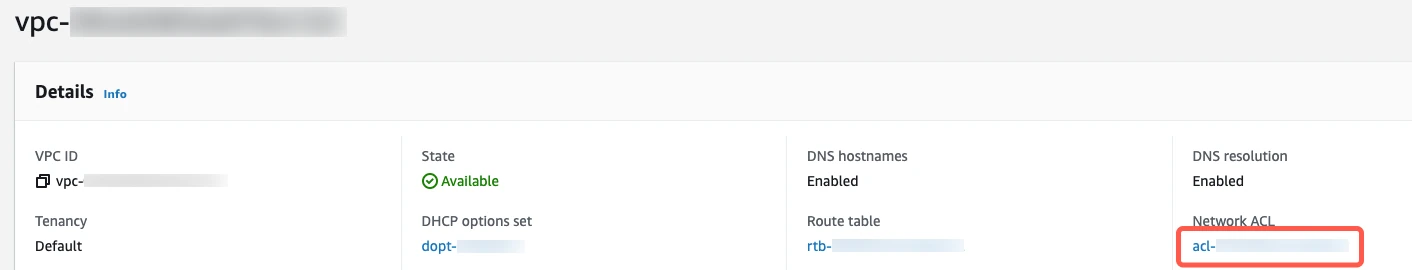
On the Network ACLs page, click the Network ACL ID.
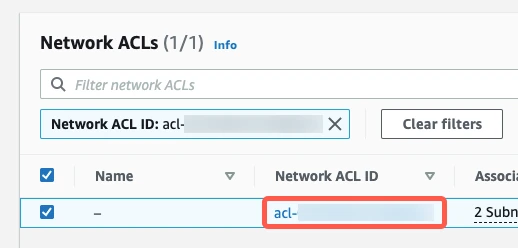
You will see tabs for Inbound Rules and Outbound Rules. You must edit both.
Edit inbound rules
Go to the Inbound Rules tab.
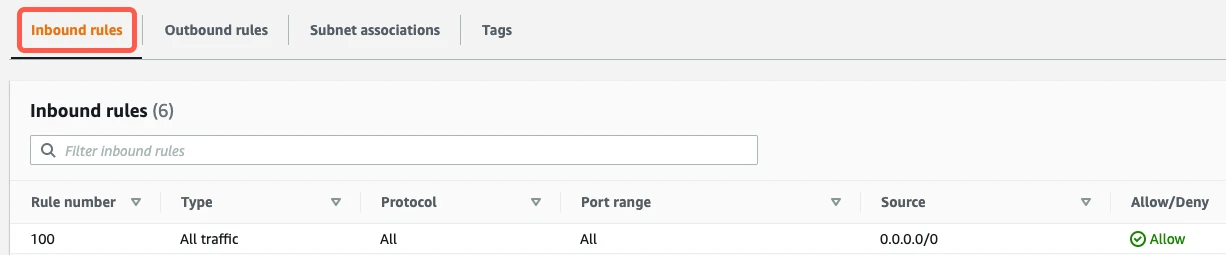
If you have a default VPC that was automatically created by AWS, the settings already allow all incoming traffic. To verify that the settings allow incoming traffic, confirm that the Source value is
0.0.0.0/0and that the ALLOW entry is listed above the DENY entry.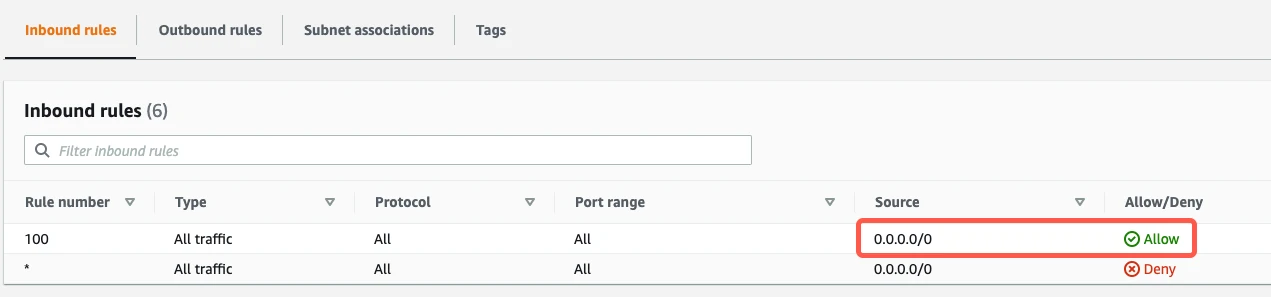
If your inbound rules don't include
ALL - 0.0.0.0/0 - ALLOWentry, edit the rules to allow the Source to access the port number of your database instance. (The port will be3306for direct connections, unless you changed the default.) What you enter in the Source field depends on whether you're connecting directly or using an SSH tunnel.- If you're connecting directly, enter Fivetran's IPs for your database's region.
- If you're connecting using an SSH tunnel, enter
{your-ssh-tunnel-server-ip-address}/32.
For additional help, see Amazon's Network ACLs documentation.
Edit outbound rules
Go to the Outbound Rules tab.
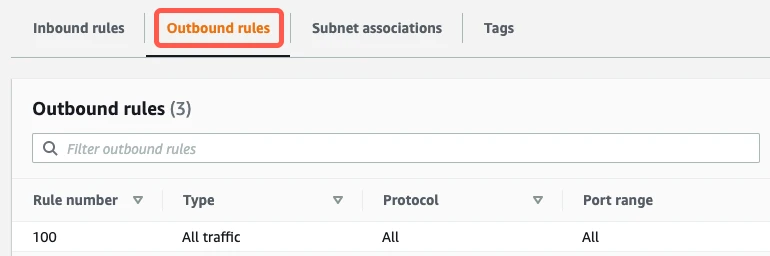
If you have a default VPC that was automatically created by AWS, the settings already allow all outbound traffic. To verify that the settings allow outbound traffic, confirm that the Destination value is
0.0.0.0/0and that the ALLOW entry is listed above the DENY entry.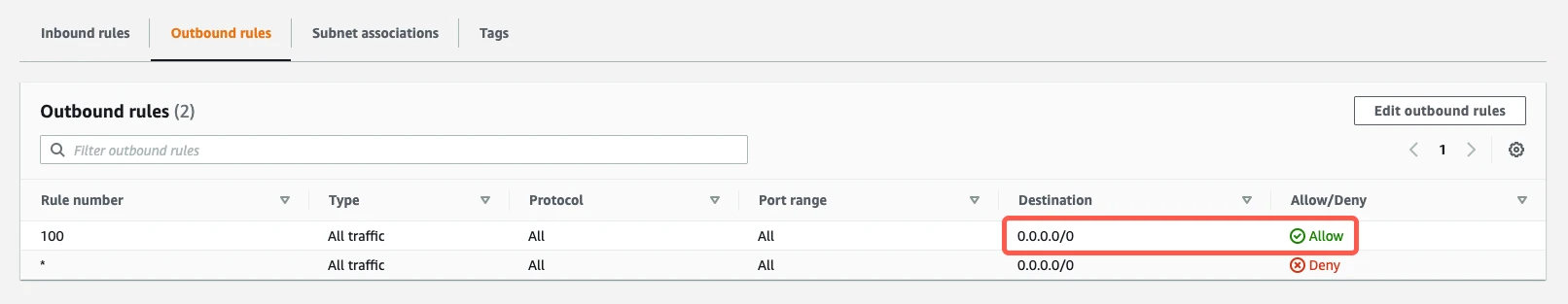
If your outbound rules don't include an
ALL - 0.0.0.0/0 - ALLOWentry, edit the rules to allow outbound traffic to all ports1024-65535for the following Destination(s):- If you're connecting directly, enter Fivetran's IPs for your database's region.
- If you're connecting using an SSH tunnel, enter
{your-ssh-tunnel-server-ip-address}/32.
Create user and configure incremental updates
In your MariaDB primary database, create a dedicated database user for Fivetran.
You cannot create users on a read replica because it is read-only. Once created on the primary, the user will automatically replicate to any read replicas.
The user must be:
- Reserved for Fivetran use only
- Unique to your connection
How you create a user depends on which incremental sync method you've chosen in Step 3. Follow the instructions below for your chosen method.
Binary log
Create a Fivetran database user
Open a connection to your primary database using your preferred SQL client (for example, MySQL Workbench or the
mysqlcommand in your operating system's terminal window).Create a Fivetran user using one of the following commands, depending on your authentication method:
For password authentication, execute the following SQL command. Replace
<username>and<password>with a username and password of your choice:CREATE USER '<username>'@'%' IDENTIFIED VIA mysql_native_password USING '<password>';For IAM authentication, execute the following SQL command. Replace
<username>with a username that matches the{db-user-name}from Step 2.CREATE USER '<username>'@'%' IDENTIFIED WITH AWSAuthenticationPlugin AS 'RDS';
Assign required permissions to the Fivetran user
Grant the following privileges to the Fivetran user you created in the previous step:
GRANT SELECT, REPLICATION CLIENT, REPLICATION SLAVE ON *.* TO '<username>'@'%'; GRANT SELECT ON mysql.rds_heartbeat2 TO '<username>'@'%'; GRANT SELECT ON mysql.rds_configuration TO '<username>'@'%'; GRANT EXECUTE ON PROCEDURE mysql.rds_kill TO '<username>'@'%';
Why these permissions are needed:
Fivetran requires
SELECTpermissions for all columns in the tables you want to sync. If we don’t have full column access, we trigger a full re-sync for that table, which can significantly slow down your sync process. If you prefer not to sync certain columns, you can exclude them directly in the Fivetran dashboard instead of limitingSELECTaccess at the database level.Granting access to
mysql.rds_heartbeat2allows Fivetran to verify that the connector is correctly configured for your RDS database. Access tomysql.rds_configurationis also required to read sync interval settings and ensure proper incremental sync behavior.Granting
EXECUTE ON PROCEDURE mysql.rds_killis optional but recommended. This privilege allows Fivetran to terminate idle or orphaned connections that it creates but no longer needs. If you omit this grant, syncs can still succeed; however, you may occasionally need to manually close unused connections on your database.
Make sure these commands complete without any errors. If there are errors, you may lack sufficient privileges and should contact your database administrator.
Configure binary logging
Update your database's default RDS configuration to enable binary logging. We need binary logs to perform incremental updates.
You only need to apply the following configurations to the databases that you want to connect to Fivetran.
Change binary logging format
Go to the AWS RDS Console and click Parameter groups.

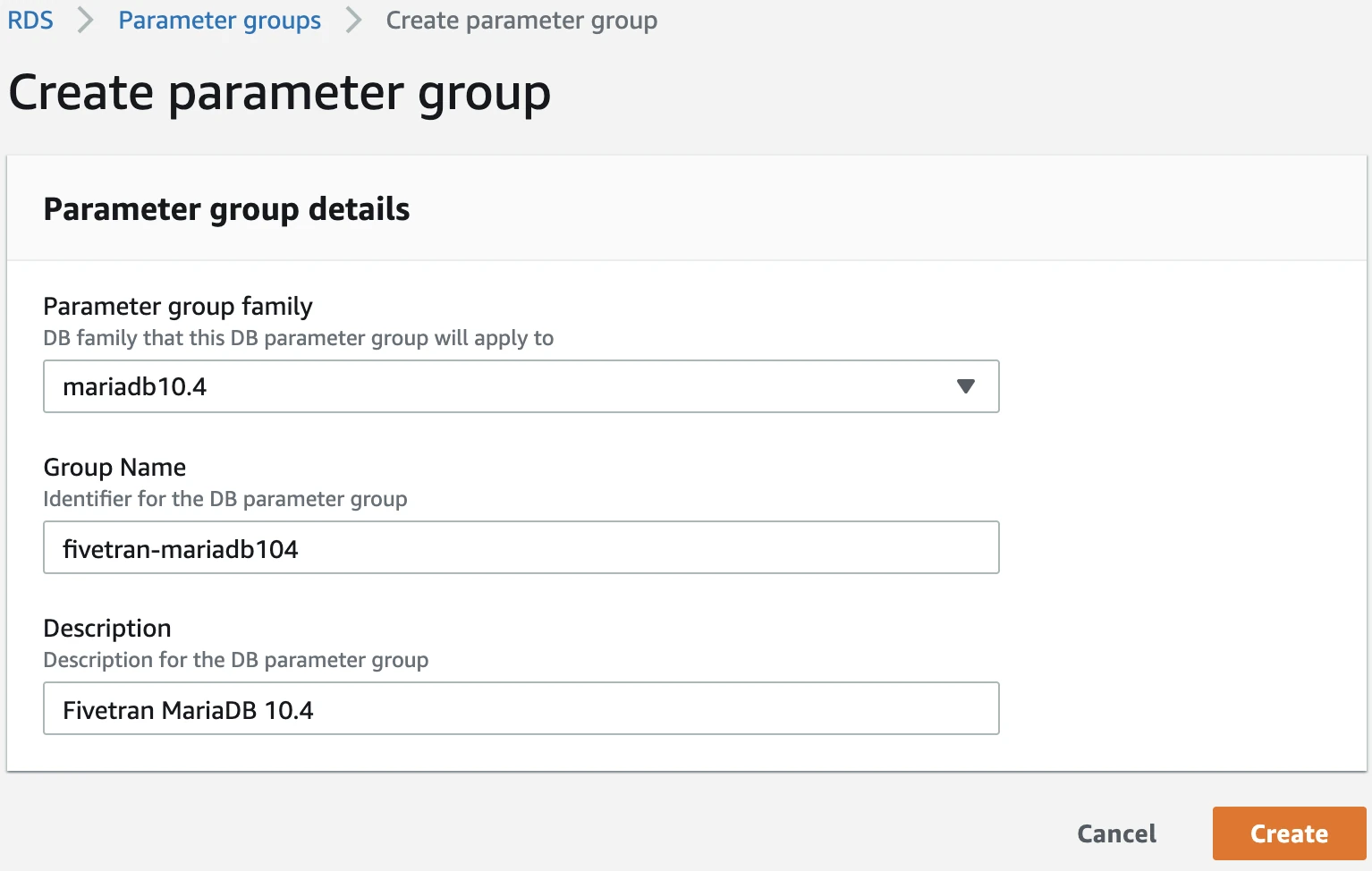
Click Create parameter group.
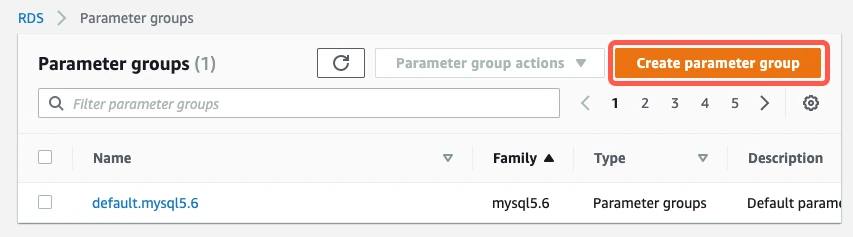
On the Create parameter group page, enter the following information:
- In the Parameter group family drop-down menu, choose the most current major version for your database. For example, if your database version is 10.4.13, your parameter group family value would be
mariadb10.4. - In the Group name field, enter a name for the parameter group.
- In the Description field, enter a brief description of the parameter group.
- In the Parameter group family drop-down menu, choose the most current major version for your database. For example, if your database version is 10.4.13, your parameter group family value would be
Click Create. You will be redirected to the Parameter groups page.
Click on the new parameter group.
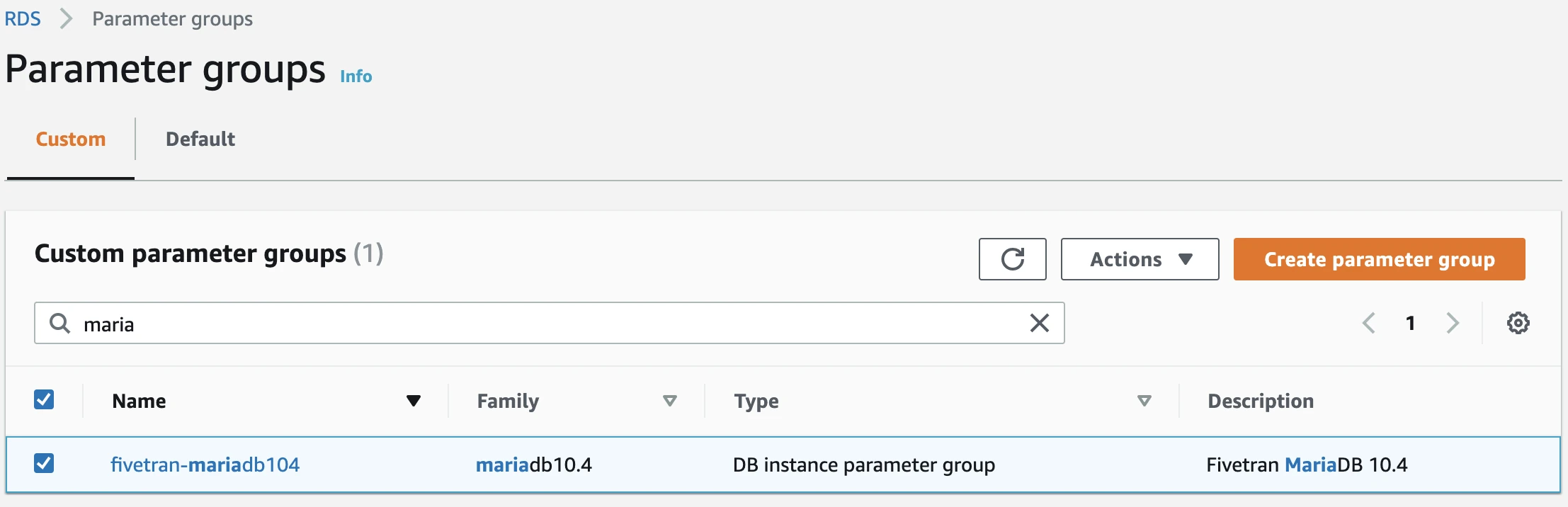
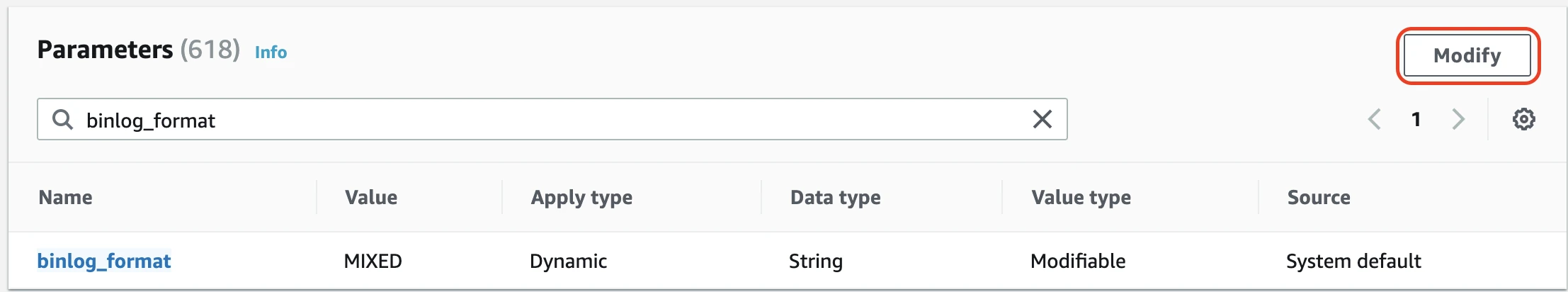
In the Parameters section, search the binlog_format parameter, then click Modify.
In the Values field, type
ROW, then clickContinue.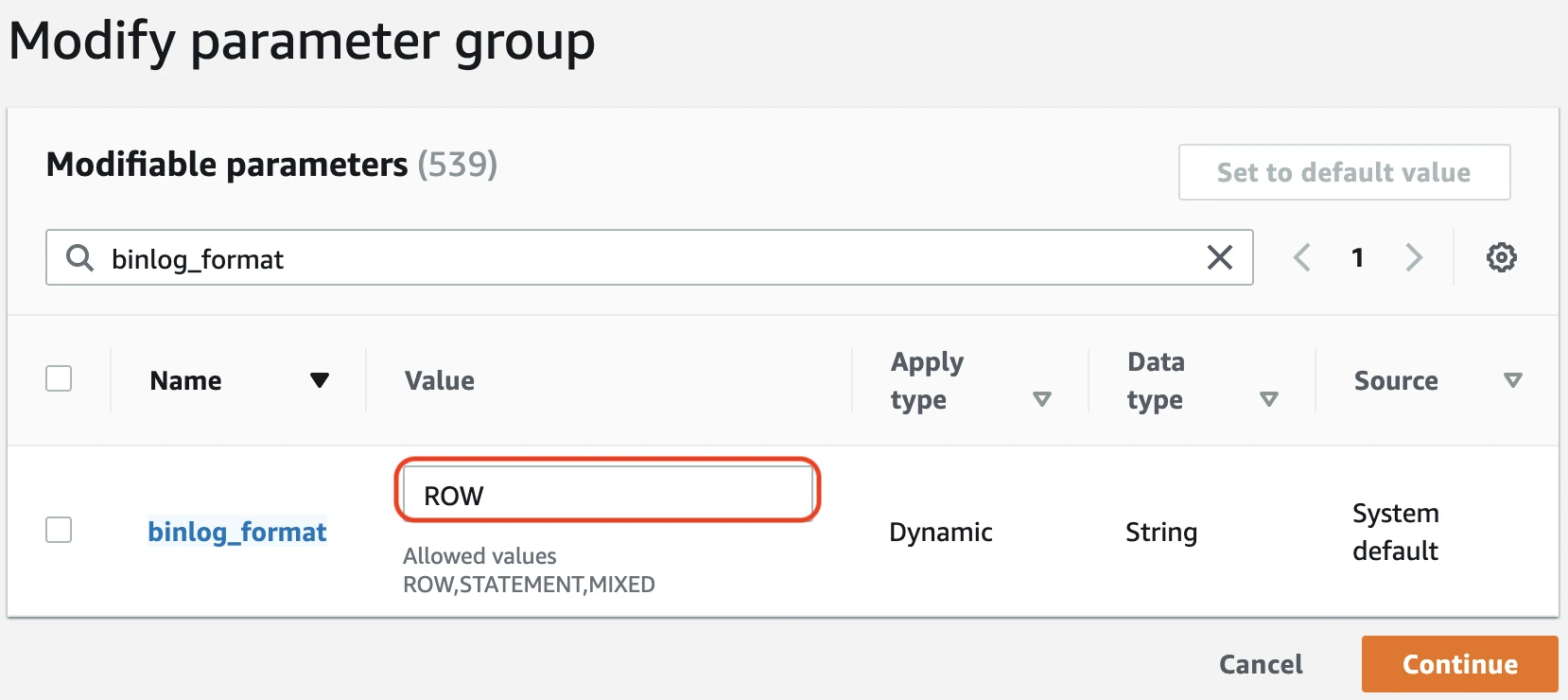
(Optional) Enable GTID mode by setting these additional parameters:
- gtid_mode to
ON - gtid_strict_mode to
ON
- gtid_mode to
Click Apply Changes.
Additional Settings (if using a read replica with history mode)
If you have connected Fivetran to a read replica and plan to run your connection in history mode, you may need to adjust several MariaDB replication parameters to avoid replication gaps and ensure correct binary log ordering.
In the RDS Console, view your read replica’s configuration.
Locate the
slave_parallel_threadsparameter.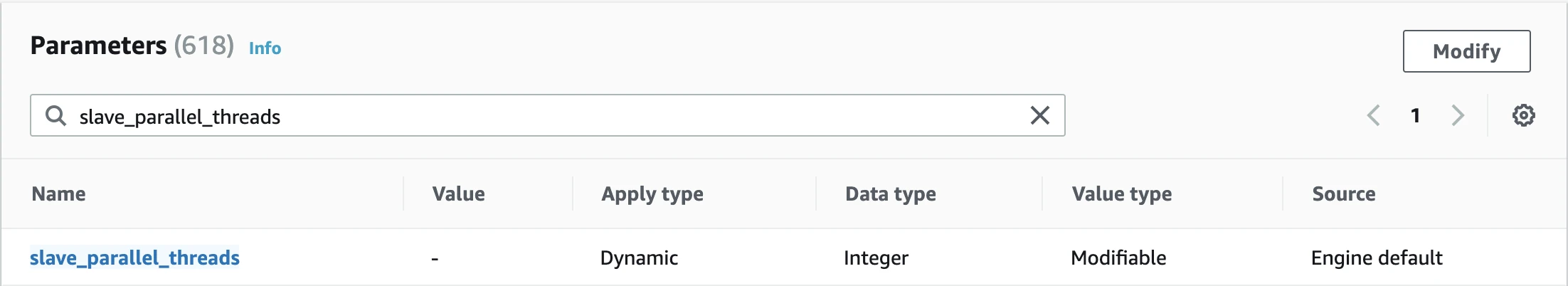
If the
slave_parallel_threadsvalue is0, no changes needed. Proceed to the Turn on automated backups section.If the
slave_parallel_threadsvalue is not0, you must set theslave_parallel_modevalue tooptimistic,conservative,aggressive, orminimalto use in-order parallel replication. Learn more about in-order parallel replication in MariaDB's parallel replication documentation.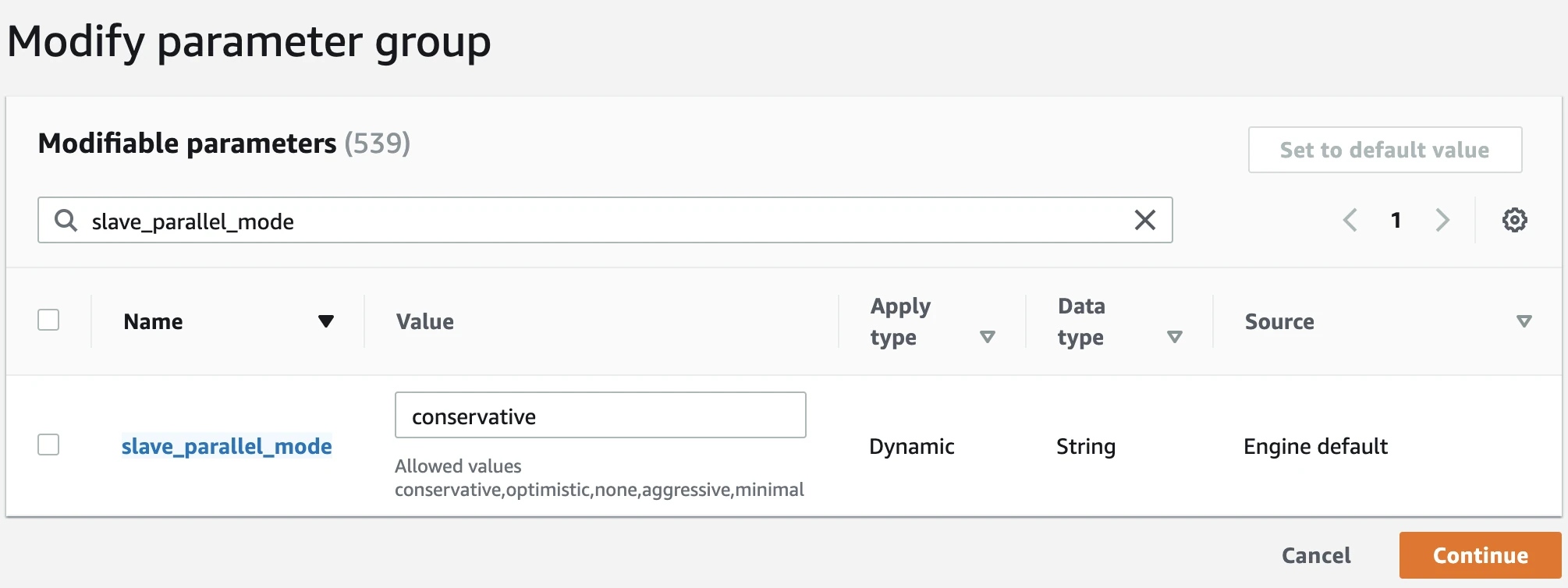
During in-order parallel replication, the transactions are executed from the relay logs on a replica in the same order as they happen on the primary database. It is very important to preserve the order of the events in the binary log, because Fivetran assumes that your binary log events are in sequential order during incremental updates.
Turn on automated backups
In the AWS RDS Console, click Databases in the left menu.

Select your MariaDB database, then click Modify.
In the Modify DB Instance screen, scroll down to find the Additional configurations section.
Set the DB Parameter Group value to the one you created.
Scroll down to Backup.
Set the Backup Retention Period to 1 day or more.
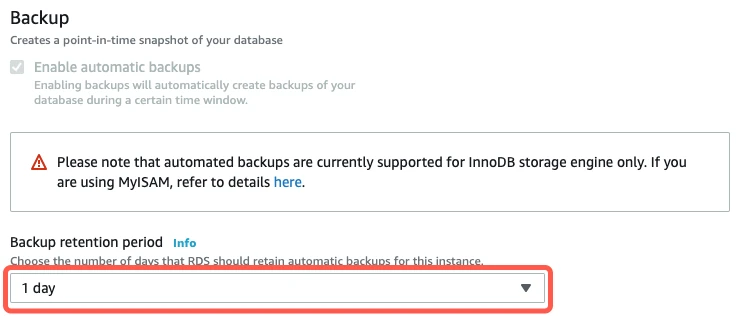
Click Continue.
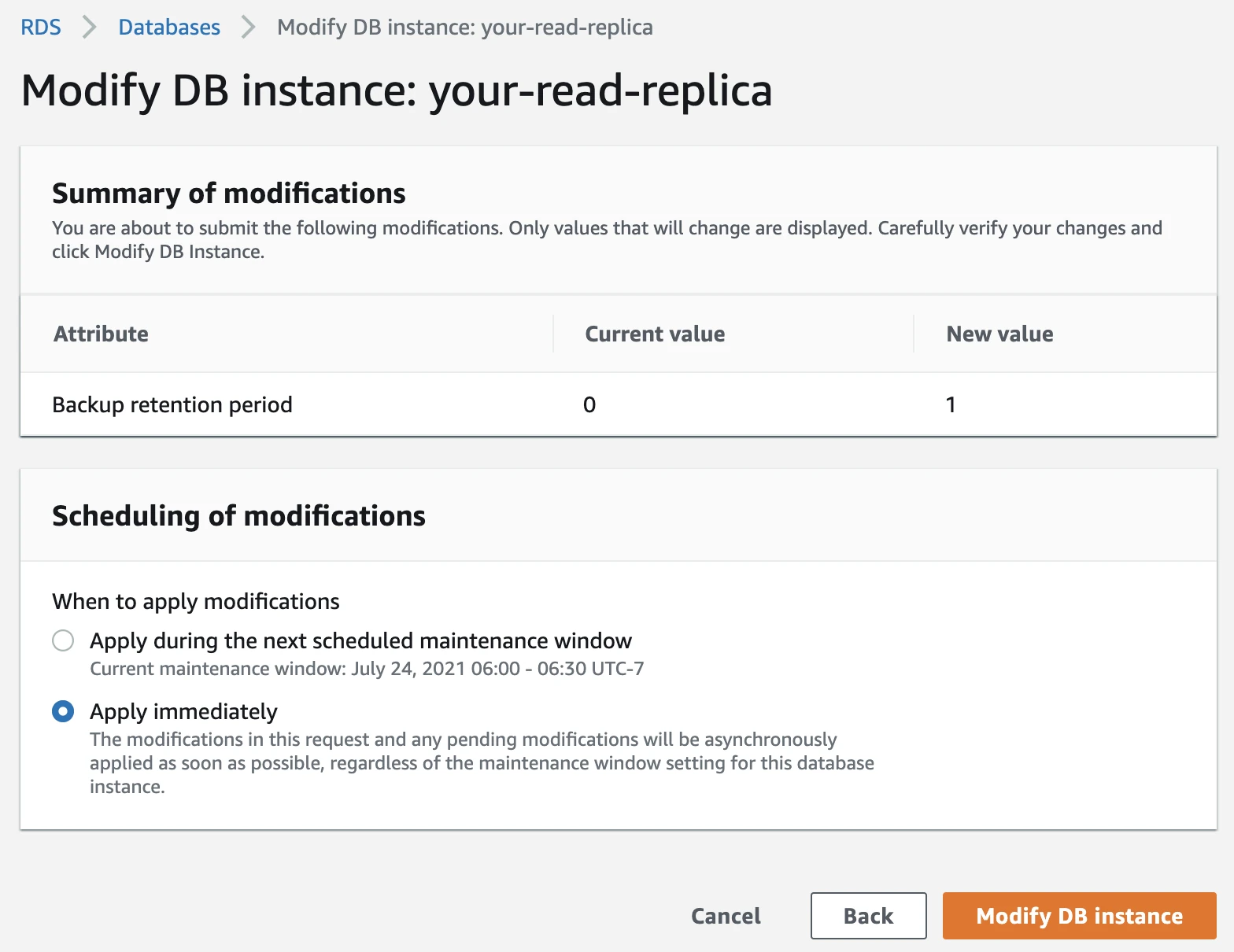
Select Apply Immediately and click Modify DB Instance.
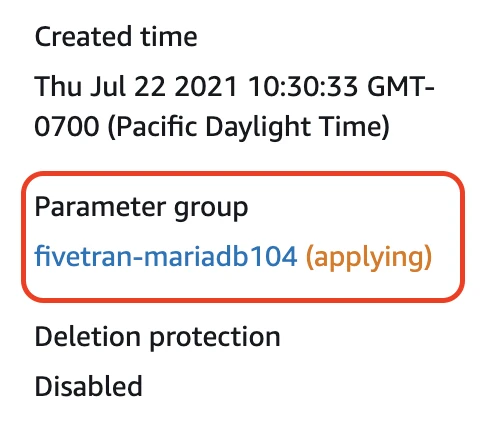
The Parameter Group setting in the database details should now show the name of your new parameter group. The Parameter Group status will say "applying" at first. Wait until the status changes to "pending-reboot."
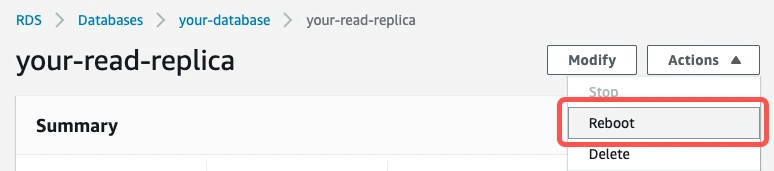
For the changes to take effect, reboot your instance by clicking Actions > Reboot.
Click Confirm to reboot the instance.
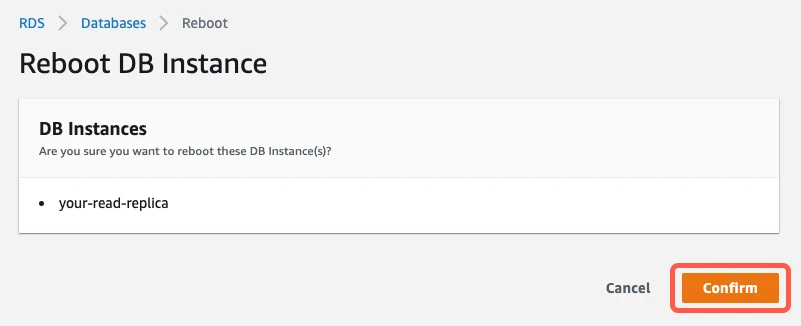
Rebooting takes a few minutes. The configuration change is complete when the database's status changes to "available" and the parameter group status changes to "in-sync."
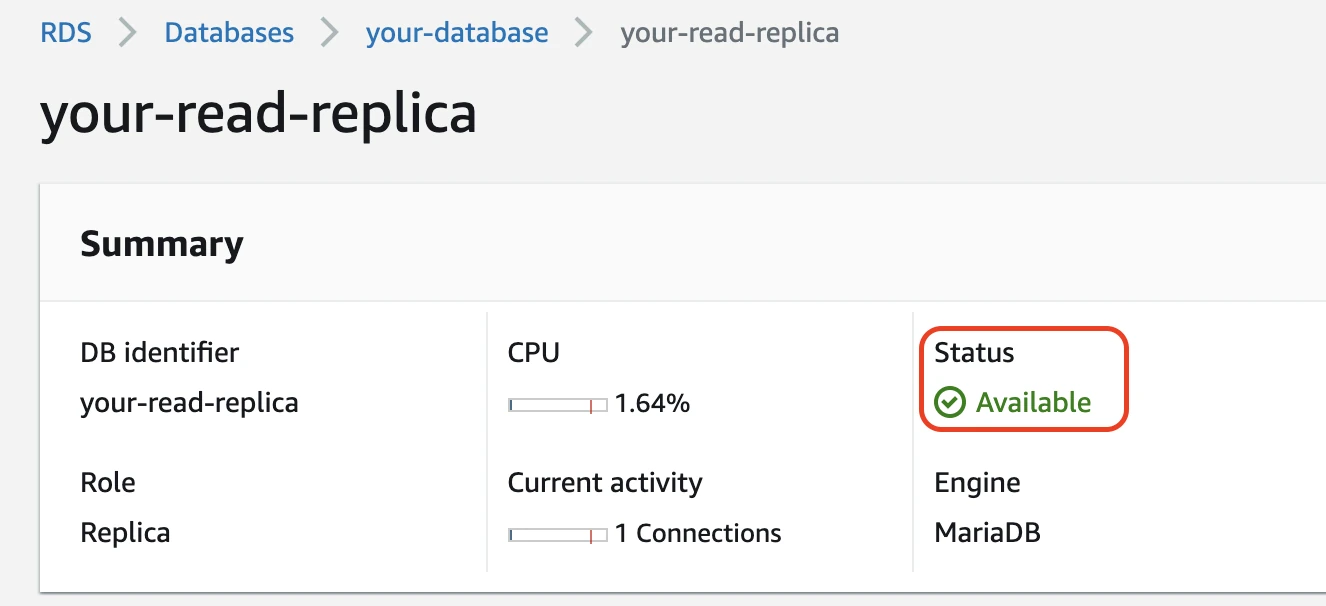
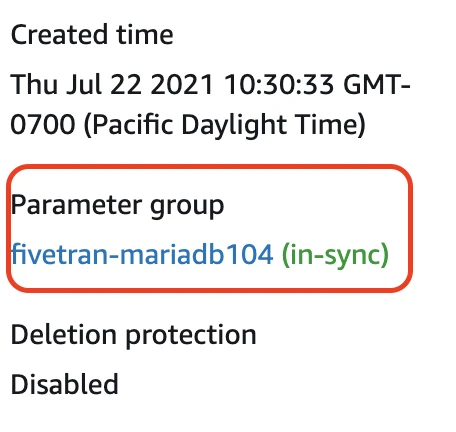
Set binary log retention period
To retain binary logs long enough for recovery or restart scenarios, Fivetran recommends setting the binary log retention period to seven days (168 hours). Run the following command on the Amazon RDS for MariaDB database that you want to connect to Fivetran:
CALL mysql.rds_set_configuration('binlog retention hours', 168);
Grant Fivetran access to binary log retention settings (optional)
During the connection setup process, Fivetran can check your binary log retention period and alert you if you need to set a longer retention period. To allow Fivetran to monitor your retention period:
GRANT SELECT ON mysql.rds_configuration to '<username>'@'%';
Fivetran Teleport Sync
Open a connection to your primary database using your preferred SQL client (for example, MariaDB Client, DBeaver, MySQL Workbench or the
mysqlcommand-line tool).Create a Fivetran user using one of the following commands, depending on your authentication method:
For password authentication, execute the following SQL command. Replace
<username>and<password>with a username and password of your choice:CREATE USER '<username>'@'%' IDENTIFIED VIA mysql_native_password USING '<password>';For IAM authentication, execute the following SQL command. Replace
<username>with a username that matches the{db-user-name}from Step 2.CREATE USER '<username>'@'%' IDENTIFIED WITH AWSAuthenticationPlugin AS 'RDS';
Grant permissions to the Fivetran user created in the previous step.
Option 1 - Grant
SELECTon all tables and columns:GRANT SELECT ON *.* TO '<username>'@'%';Option 2 - Grant
SELECTon specific tables or columns only:GRANT SELECT ON <your_database.your_table> TO '<username>'@'%';-- For column-level control GRANT SELECT (<column1>, <column2>) ON <your_database.your_table> TO '<username>'@'%';Optional - Allow Fivetran to terminate its own stale sessions:
GRANT EXECUTE ON PROCEDURE mysql.rds_kill TO '<username>'@'%';
Make sure these commands complete without any errors. If there are errors, you may lack sufficient privileges and should contact your database administrator.
Finish Fivetran configuration
In your connection setup form, enter a Destination schema prefix of your choice. This is used as the connection name and cannot be modified once the connection is created.
In the Destination schema names field, choose the naming convention you want Fivetran to use for the schemas, tables, and columns in your destination:
- Source naming: Preserves the original schema, table, and column names from the source system in your destination.
- Fivetran naming: Standardizes the schema, table, and column names in your destination according to the Fivetran naming conventions.
If you want to modify your selection, make sure you do it before you start the initial sync.
Depending on your selection, we will either prefix the connection name to each replicated schema or use the source schema names instead.
(Hybrid Deployment only) If your destination is configured for Hybrid Deployment, the Hybrid Deployment Agent associated with your destination is pre-selected for the connection. To assign a different agent, click Replace agent, select the agent you want to use, and click Use Agent.
(Not applicable to Hybrid Deployment) Choose your Connection method. If you selected Connect via an SSH tunnel, copy or make a note of the Public Key and add it to the
authorized_keysfile while configuring the SSH tunnel, and provide the following information:- SSH hostname (do not use a load balancer's IP address/hostname)
- SSH port
- SSH user
- If you enabled TLS on your database in Step 1, make sure to keep the Require TLS through Tunnel toggle turned ON.
In the Host field, enter your database host's IP (for example,
1.2.3.4) or domain (for example,your-database.cp0rdhwjbsae.us-east-1.rds.amazonaws.com)Enter your database instance's Port number (usually
3306).Choose your Authentication Method:
For PASSWORD authentication, enter the following details:
- User: The Fivetran-specific database user you created in Step 6.
- Password: The corresponding password for that user.
For IAM authentication, enter the following details:
- AWS region code: The region where your RDS instance is hosted.
- Role ARN (Not applicable to Hybrid Deployment): The ARN of the IAM role you created in Step 2.
- Database User: The Fivetran-specific IAM-enabled user from Step 6.
(Optional for Hybrid Deployment) If you want to use a TLS connection between your Hybrid Deployment Agent and Fivetran cloud, set the Require TLS toggle to ON.
Before you set this toggle to ON, you must first enable TLS on your database. Learn how in the Security section of the MariaDB reference manual for your database version.
Under Update Method, choose how Fivetran will detect data changes in your source database:
- Read Changes via Binary Log - Reads directly from the MariaDB binary log using Fivetran's Binary log incremental sync method.
- Detect Changes via Fivetran Teleport Sync - Detects changes by comparing source and snapshot data using Fivetran Teleport Sync incremental sync method.
(Binary log only) Enter a unique Replica ID for Fivetran. We provide a random replica ID, but you can provide your own if you'd prefer or if the setup form's replica ID conflicts with one of your existing replica IDs.
(Not applicable to Hybrid Deployment) Copy the Fivetran's IP addresses (or CIDR) that you must safelist in your firewall.
Click Save & Test. Fivetran tests and validates our connection to your Amazon RDS for MariaDB database. Upon successful completion of the setup tests, you can sync your data using Fivetran.
Setup tests
Fivetran performs the following tests to ensure that we can connect to your Amazon RDS for MariaDB database and that it is properly configured:
- The Connecting to SSH Tunnel Test validates the SSH tunnel details you provided in the setup form. It generates a pop-up window where you must verify the SSH fingerprint. It then checks that we can connect to your database using the SSH Tunnel. (We skip this test if you are connecting directly.)
- The Connecting to Host Test verifies that the database host is not private and checks that we can connect to the host.
- (IAM authentication only) The Generating IAM Authentication Token test verifies that Fivetran can use the provided IAM credentials to generate an authentication token for the database.
- The Validating TLS Connection to Source Database Test validates the server certificate and checks that we can connect to your database using TLS. An untrusted certificate generates a pop-up window where you must choose which certificate you want Fivetran to use. (We skip this test if you selected an indirect connection method and then disabled the Require TLS through Tunnel toggle.)
- The Validating Database User Test validates the database credentials you provided in the setup form.
- The Checking Database Configuration Test verifies that we can find your database's server ID. It then checks your binary log configuration and confirms that we can connect to the binary log.
- The Validating Database Type Test checks that your database type matches the connector type. For example, this test will generate a warning if you try to set up a generic MariaDB connection with a Amazon RDS for MariaDB database.
- The Checking Binlog Retention Period Test verifies that your binary log is set to retain at least 1 day's worth of changes.
The tests may take a few minutes to finish running.