AWS PrivateLink
You must have a Business Critical plan to use AWS PrivateLink.
AWS PrivateLink allows VPCs and AWS-hosted or on-premises services to communicate with one another without exposing traffic to the public internet. PrivateLink is the most secure connection method. Learn more in AWS’ PrivateLink documentation.
Fivetran uses PrivateLink to move your data securely between our system and your AWS-hosted or on-premises source. PrivateLink works differently depending on your source type:
- If your data source is hosted in AWS, Fivetran can connect to your source using a PrivateLink connection. We query and process the data from the source into our system.
- If your data source is hosted on-premises, Fivetran can use AWS Direct Connect to access your source data. AWS Direct Connect establishes a private network connection between your premises and an AWS VPC. We connect to that AWS VPC using a PrivateLink connection, then query and process the data from the source into our system. Learn more in AWS’ Direct Connect documentation.
You can also use AWS Private Link with multiple destinations. See a complete list in our Supported destinations documentation.
As an extra layer of security, Fivetran enables TLS on your PrivateLink connection by default. We recommend that you keep TLS enabled unless you know it is safe to forgo it. To disable TLS, set the Require TLS when using Private Networking toggle to OFF.
If you set the Require TLS when using Private Networking toggle to OFF, Fivetran first attempts to connect over TLS. If this fails, Fivetran automatically retries the connection in clear text. You are responsible for configuring this option according to your corporate security policies.
Prerequisites
To set up AWS PrivateLink, you need an AWS-hosted source (EC2, RDS, or S3 only) or an on-premises source in one of our supported regions. If your source is on-premises, it must be one of our supported databases.
How you connect AWS PrivateLink to your source depends on whether your source is hosted in AWS or on-premises.
Postrequisites
To use AWS PrivateLink, you must select AWS as a Cloud service provider in the Finish Fivetran configuration step of the relevant destination setup guide.
Setup instructions for AWS-hosted source
Expand for instructions
We support connecting to the following AWS-hosted sources using PrivateLink:
Third-party managed database services, such as MongoDB Atlas, may not be supported. Create a Fivetran support ticket to confirm if your managed database service is supported.
| AWS Host | Supported Connectors |
|---|---|
| Amazon Aurora | MySQL PostgreSQL |
| Amazon EC2 | Amazon DynamoDB Amazon DocumentDB MariaDB MongoDB MySQL Oracle PostgreSQL SAP ERP on HANA SAP OData SQL Server |
| Amazon RDS | Amazon RDS for MariaDB Amazon RDS for MySQL Amazon RDS for Oracle Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL Amazon RDS for SQL Server |
| Other | Amazon S3 AWS Lambda Salesforce |
Amazon S3 does not require any configuration. If your S3 bucket is in the same region as your Fivetran account, your network traffic does not traverse the public Internet. The Amazon S3 Gateway Endpoints ensure that regional traffic stays within the AWS network.
You must have an AWS endpoint service configured for your source before you set up a PrivateLink connection with Fivetran. AWS endpoint services only work with network load balancers (NLB), so you must create an NLB inside your VPC if you do not already have one. The NLB receives requests from Fivetran and routes it to your source.
The following graphic illustrates how Fivetran connects to the customer database using AWS Private Link:
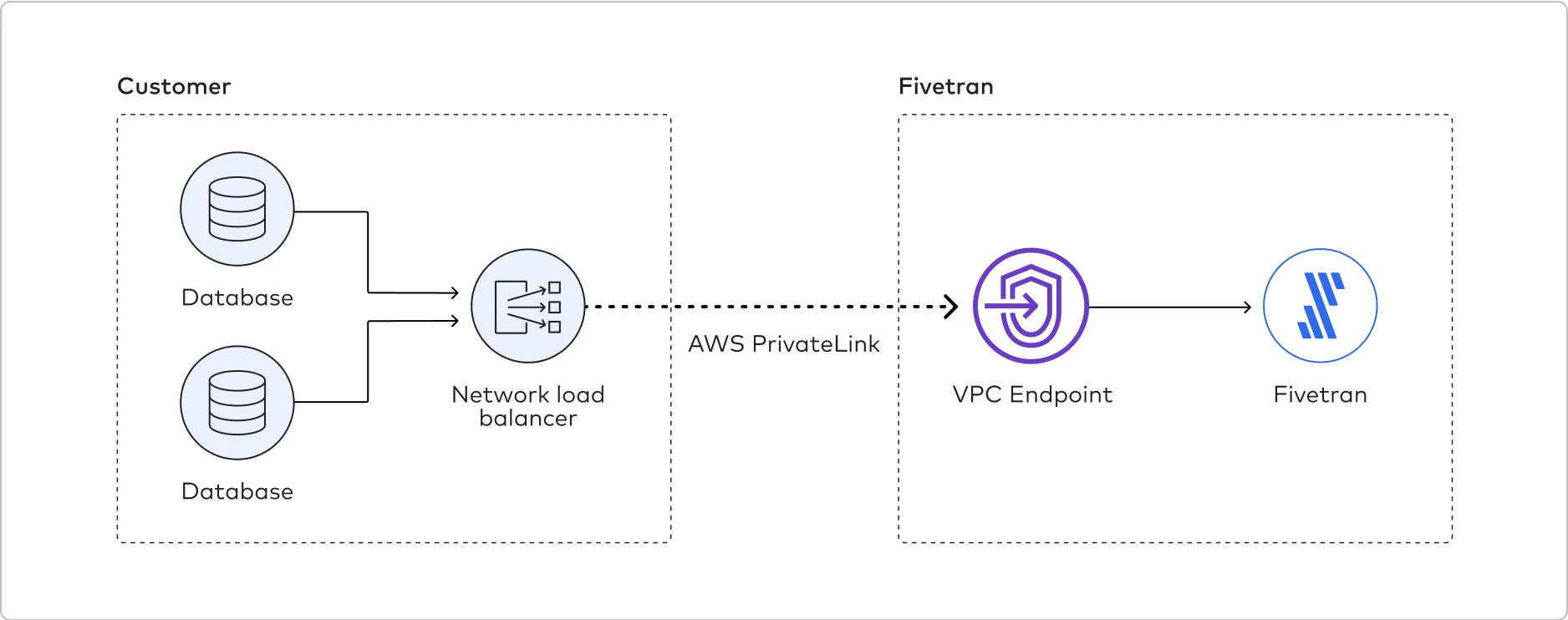
Since endpoint service configurations are out of Fivetran’s control, we recommend that you contact your AWS representatives for help setting up PrivateLink. However, we do provide the following high-level instructions based on how customers typically configure their data sources:
In your VPC, create an NLB for your data source and configure it for each subnet (availability zone) in which the service should be available. For help, see the Create an NLB section.
Skip this step if your data source is already running behind an NLB.
If you choose to use security groups with your NLB, you must allow the following Fivetran's internal CIDR range on the security groups:
10.0.0.0/8.Create a VPC endpoint service configuration and specify your NLB.
Make sure that you are familiar with the endpoint service considerations and have met its prerequisites.
Safelist Fivetran’s AWS VPC Account ID (
arn:aws:iam::834469178297:root) to allow access to your VPC endpoint service.To learn how to safelist the Fivetran account ID, see AWS’ endpoint service permission documentation.
Create a Fivetran support ticket and provide the service name (VPCe) (for example,
com.amazonaws.vpce.<region_id>.vpce-svc-xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx) along with the hostname of the service/source. Fivetran will then finish the setup on our side.To activate the connection, accept the interface endpoint connection request from Fivetran. By default, connection requests must be manually accepted. However, you can configure the acceptance settings for your endpoint service so that any connection requests are automatically accepted.
Create an NLB
On a single static IP service (EC2, non-RDS database, etc.)
To create an NLB on a single static IP service, follow the instructions in AWS’ creating a network load balancer documentation. Either ensure that the NLB availability zones match the target availability zones or enable cross-zone load balancing.
On a dynamic IP service (Amazon Aurora database, RDS database, etc.)
NLB can only route traffic to an EC2 instance, an IP address, or a Lambda function through target groups. Since Aurora and RDS databases don’t have a dedicated IP address or EC2 instance ID, there are two different ways to configure an NLB to route traffic to these databases - using a port forwarding instance or using the IP address (dynamic IP address) of the database. Follow the instructions below for your chosen method.
Using a port forwarding instance
You must deploy an EC2 instance that is configured to do port forwarding (accepting requests from the NLB and forwarding those requests to the RDS database). Here is a sample script that you can use to set up the EC2 port forwarding instance:
#!/bin/bash PREVLOGFILE=/root/ip.txt # Note the below section of the code is important in the event of a server restart. if test -f "$PREVLOGFILE"; then truncate -s 0 $PREVLOGFILE echo "State file $PREVLOGFILE has been emptied" fi python -m SimpleHTTPServer 801 & # NOTE: USE PORT 801 FOR <HEALTH_CHECKS> PARAMETER BELOW echo 1 -> /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward export RDS_ENDPOINT=<<PROSPECT RDS INSTANCE ENDPOINT>> #NOTE: DO NOT INCLUDE THE <<>> CHARACTERS, NO QUOTATION MARKS. export RDS_PORT=<<PROSPECTS RDS INSTANCE PORT>> #NOTE: DO NOT INCLUDE THE <<>> CHARACTERS, NO QUOTATION MARKS. iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -j MASQUERADE while true do LOGFILE=/root/ip.txt Current_IP=$(dig +short $RDS_ENDPOINT | tail -n1) #NOTE: THE "/ TAIL -n1" piece is critical to ensure only the IP address of the RDS instnce is picked. if [ $LOGFILE = "" ] ; then iptables -I INPUT -i eth1 -s $Current_IP -j ACCEPT echo $Current_IP > $LOGFILE else Old_IP=$(cat $LOGFILE) if [ "$Current_IP" = "$Old_IP" ] ; then echo "IP address has not changed ($Old_IP -> $Current_IP)" else iptables -t nat -D PREROUTING -p tcp --dport 80 -j DNAT --to-destination $Old_IP:$RDS_PORT iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp --dport 80 -j DNAT --to-destination $Current_IP:$RDS_PORT sysctl net.ipv4.ip_forward=1 iptables-save echo $Current_IP > $LOGFILE echo "IP address has changed ($Old_IP -> $Current_IP)" fi fi sleep 5 doneIf you are using Amazon Linux 2023, this doesn't support python2. You need to change the following part of Line 6 of the script above from:
python -m SimpleHTTPServer 801to:
python3 -m http.server 801Once you’ve finished setting up the port forwarding instance, configure the NLB listener and target group to route traffic to the portforwarder EC2 instance.
Using the dynamic IP address
Aurora and RDS databases provide an endpoint to access your database when you set them up. This endpoint resolves to an IP address. AWS doesn’t recommend using this IP address, since it can change without notice. To work around this limitation, you can deploy a lambda function to periodically check the IP address and update the NLB target group when it changes.
To use the IP address of the RDS or Aurora database in your NLB target group, do the following:
Run the
nslookupordigcommand with the domain name of RDS endpoint as the input to find the IP address:dig +short <YOUR_RDS_DNS_ENDPOINT>Set up your NLB target group with the IP address.
Deploy a lambda function to periodically perform
nslookupon the RDS endpoint to see if the IP address has changed and update the target group with the new IP address.
Setup instructions for on-premises source
Expand for instructions
Create a Fivetran support ticket for assistance with setting up PrivateLink for your on-premises source. Our team will help you set up AWS Direct Connect to an AWS VPC, which Fivetran can connect to using PrivateLink.
Setup instructions for self-service Fivetran accounts Beta
Expand for instructions
Self-service Private Link lets you create and manage AWS PrivateLinks without waiting for Fivetran support to provision the network infrastructure.
Self-service Private Link is supported with AWS PrivateLink for the following connectors:
Find connection service name
Log in to your AWS account.
Configure the NLB for each subnet (availability zone) where you want the service to be available.
Create a VPC endpoint service configuration and specify your NLB.
Make sure that you are familiar with the endpoint service considerations and you have met its prerequisites.
Safelist Fivetran’s AWS VPC Account ID (
arn:aws:iam::834469178297:root) to allow access to your VPC endpoint service.To learn how to safelist the Fivetran account ID, see AWS' documentation.
Make a note of your service name (VPCe) (for example,
com.amazonaws.vpce.<region_id>.vpce-svc-xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx). You will need it to configure Fivetran.
Configure PrivateLink connection
In Fivetran's connection setup form, select Connect via Private Networking in the Connection Method drop-down menu.
Click + Configure a new PrivateLink connection.
Enter a Name for your PrivateLink connection.
In the PrivateLink connection service name field, enter the service name you found in Step 1.
Click Create and save. Fivetran will raise a connection request in AWS.
It might take up to 10 minutes for us to raise the connection request.
Accept connection request
Go to your AWS account.
In the top left corner, click Services, then select VPC.
In the VPC dashboard, click Endpoint services.
Refresh the Endpoint services page to see the new connection request from Fivetran. The new connection request is in Pending acceptance state.
It might take some time for the new connection request to appear on the list.
Select the new connection request.
Go the Endpoint connections tab.
In the Actions drop-down menu, select Accept endpoint connection request.
In the Accept endpoint connection request pop-up window, enter
acceptin the text box, then click Accept. The status of the request will change to Pending. After a few minutes, the status will change to Accepted, and a Connection created message will appear in Fivetran's connection setup form.