Google Cloud Private Service Connect
You must have a Business Critical plan to use Google Cloud Private Service Connect.
Google Cloud Private Service Connect allows VPCs and Google-hosted or on-premises services to communicate with one another without exposing traffic to the public internet.
Fivetran uses Private Service Connect to move your data securely between our system and your Google Cloud-hosted destination.
By default, Fivetran enables TLS on your Private Service Connect connection for an extra layer of security. We recommend that you keep TLS enabled unless you know it is safe to disable it. To disable TLS, set the Require TLS when using Private Service Connect toggle to OFF.
If you set the Require TLS when using Private Service Connect toggle to OFF, Fivetran first attempts to connect over TLS. If this fails, Fivetran automatically retries the connection in clear text. You are responsible for configuring this option according to your corporate security policies.
Architecture
The following graphic illustrates how Fivetran connects to a destination using Google Cloud Private Service Connect:
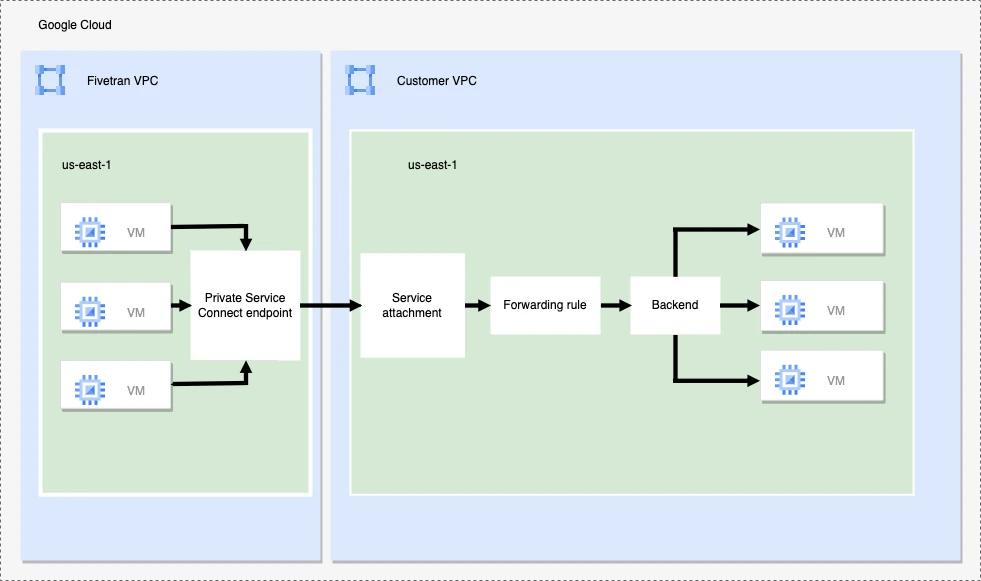
Supported destinations
We support Private Service Connect for the following destinations:
The setup instructions below are not applicable to Snowflake destinations. To connect a Snowflake destination using Google Cloud Private Service Connect, see our Snowflake setup guide.
Prerequisites
To set up Google Cloud Private Service Connect, you need a GCP-hosted destination and a Fivetran instance running in one of our supported regions.
Setup instructions for Google Cloud Private Service Connect
Expand for instructions
We support connecting to any GCP-hosted resource as long as it is supported by Fivetran and exposed through Private Service Connect producer.
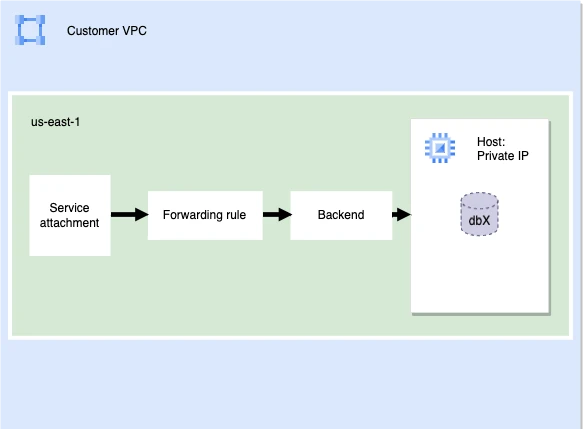
In the following example, we publish a service that runs on a specific instance. However, there are several other ways to expose your service. To learn more, contact your administrators or read Google's documentation.
You need the following as inputs for the commands used in the steps below:
<NETWORK>- VPC network in which the exposed resource exists<SUBNET>- Subnetwork where the exposed resource exists<ILB_SUBNET>- Subnetwork used for allocation of internal load balancer addresses (forwarding rules)<PSC_NAT_SUBNET>- Subnetwork used for allocation IPs for each customer endpoint address<REGION>- Region where the exposed resource exists<ZONE>- Zone where the exposed resource exists<VM_NAME>- VM on which the exposed resource runs<VM_IP>- Private IP on which the exposed resource is available<RESOURCE_PORT>- Port on which the exposed resource is available in a VM<NETWORK_ENDPOINT_GROUP>- Network endpoint group<HEALTH_CHECKS>- Port health checks<BACKEND_SERVICES>- Backend services<FORWARDING_RULE>- Forwarding rule<SERVICE_ATTACHMENT>- Service attachment
If you already have a regional internal load balancer for your resource, skip to Step 8 of this example.
Create a network endpoint group.
gcloud compute network-endpoint-groups create --network <NETWORK> --subnet <SUBNET> \ --network-endpoint-type gce-vm-ip --zone <ZONE> <NETWORK_ENDPOINT_GROUP>Add an instance with the running resource as an endpoint to the network endpoint group.
gcloud compute network-endpoint-groups update --zone <ZONE> <NETWORK_ENDPOINT_GROUP> \ --add-endpoint='instance=<VM_NAME>Create health checks to automatically enable and disable the instance. In this example, we use port checks.
gcloud compute health-checks create tcp --region <REGION> --check-interval=60s --port=<RESOURCE_PORT> <HEALTH_CHECKS>Create the backend services.
gcloud compute backend-services create --region=<REGION> --health-checks=<HEALTH_CHECKS> \ --health-checks-region=<REGION> --load-balancing-scheme=INTERNAL <BACKEND_SERVICES>Assign the network endpoint group you created at the backend.
gcloud compute backend-services add-backend <BACKEND_SERVICES> --network-endpoint-group=<NETWORK_ENDPOINT_GROUP> \ --network-endpoint-group-zone=<ZONE>(Optional) Allocate a subnetwork dedicated to forwarding rules.
cloud compute networks subnets create --network <_NETWORK_> --region <REGION> --range=10.0.X.0/24 <ILB_SUBNET>Create a forwarding rule for the internal load balancer. It points to
<BACKEND_SERVICES>and allocates the IP address from<ILB_SUBNET>in<NETWORK>.gcloud compute forwarding-rules create --backend-service=<BACKEND_SERVICES> --region <REGION> \ --load-balancing-scheme=INTERNAL --ports=ALL --subnet=<ILB_SUBNET> --network=<NETWORK> <FORWARDING_RULE>Allocate a NAT subnetwork dedicated to creating endpoints for each connected customer.
cloud compute networks subnets create --network <NETWORK> --region <REGION> --range=10.0.X.0/24 \ --purpose=PRIVATE_SERVICE_CONNECT <_PSC_NAT_SUBNET_>Open traffic from the ILB and NAT networks to a VM or port using the corresponding ranges specified in previous steps.
gcloud compute firewall-rules create --direction=INGRESS --priority=1000 --network=<_NETWORK_> --action=ALLOW \ --rules=tcp:_RESOURCE_PORT_ --source-ranges=10.0.X.0/24 --destination-ranges=<_VM_IP_>/32 db-demo-allow-psc-nats gcloud compute firewall-rules create --direction=INGRESS --priority=1000 --network=<_NETWORK_> --action=ALLOW \ --rules=tcp:_RESOURCE_PORT_ --source-ranges=10.0.X.0/24 --destination-ranges=<_VM_IP_>/32 db-demo-allow-ilb-natsCreate a service attachment and point it to the internal load balancer you created above (
FORWARDING_RULE) with manual accepting mode.gcloud compute service-attachments create --producer-forwarding-rule=<FORWARDING_RULE> --connection-preference=ACCEPT_MANUAL \ --region=<REGION> --description='Producer for my resource in region' --nat-subnets <_PSC_NAT_SUBNET_> <SERVICE_ATTACHMENT>Contact our support team to set up a Private Service Connect link in Fivetran. Fivetran will provide a
PSC_CONNECTION_ID(Private Service Connect ID), which allows you to identify the connections that come from Fivetran before you approve them. Make a note of thePSC_CONNECTION_ID. You will need it to set up your destination.
- If you want to auto-approve the Fivetran project, use the
--consumer-accept-list=fivetran_donkeys=2parameter for gcloud. - The instructions above use network endpoint groups as it is easy to attach them to existing VMs. However, if a VM is already part of the instance groups, you can use it directly as a backend services target.
- You can test a newly-created producer in another VPC by allocating an IP and creating a forwarding rule, as described in Google's documentation.
Setup instructions for Google Cloud SQL resources exposed through private service access
Expand for instructions
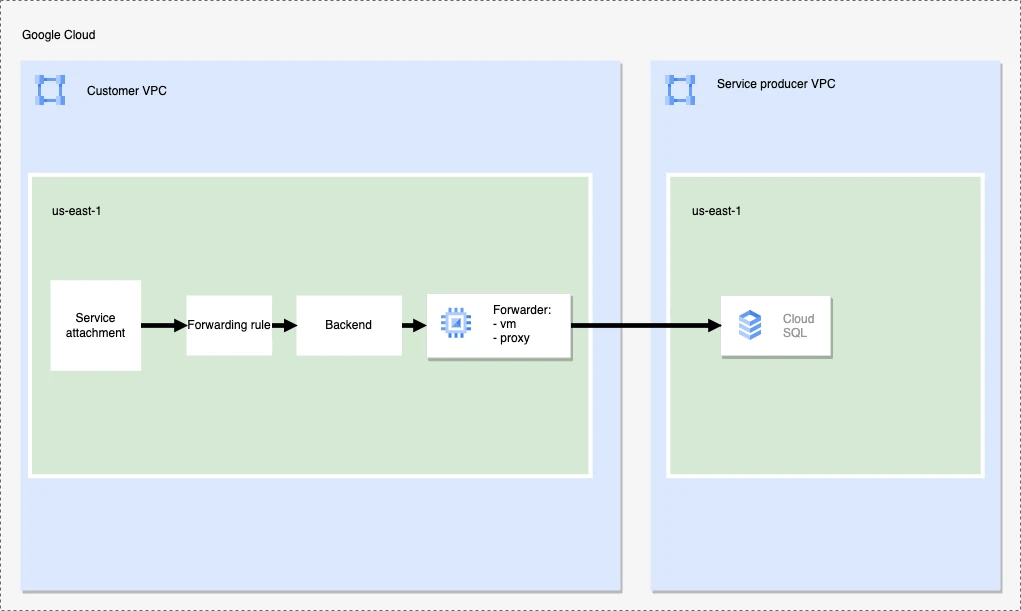
To set up access for Google Cloud SQL destinations through private IP, you need an additional VM to act as a forwarding proxy. You can use solutions like HAProxy or iptables for this.
If you use the following vm script, make sure that you persist iptables rules and consider using instance groups instead of standalone VMs.
#!/bin/bash
# This script configures Network Address Translation to forward incoming packets
# from the Load Balancer to IP-based destinations and route them
# back. In this script, "destination" means a destination server that Fivetran connects to.
# local port where the Load Balancer sends traffic to
SOURCE_PORT=<local_port>
# destination server inside internal network
DESTINATION_IP=<destination_server_ip_address>
DESTINATION_PORT=<destination_server_port>
# enable IP forwarding on host
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
# clear existing iptables rules and chains
iptables -F
iptables -t nat -F
iptables -X
# change the packet recipient from local to destination socket (host & port)
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp --dport ${SOURCE_PORT} -j DNAT --to-destination ${DESTINATION_IP}:${DESTINATION_PORT}
# change the source IP address from the LB NAT IP address to the IP of this LB-backend host
iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -p tcp -d ${DESTINATION_IP} --dport ${DESTINATION_PORT} -j SNAT --to-source $(hostname -i)
Once you set up the VMs, follow the standard setup instructions for Google Cloud Private Service Connect.
Postrequisites
To use Google Cloud Private Service Connect, you must select GCP as the Cloud service provider in the destination setup form.