Row Filtering
Row filtering enables you to only sync rows that meet user-defined criteria based on a selected table, column, and operator. We support row filtering for initial syncs, re-syncs, and incremental syncs.
When you block a table or column or hash a column that is specified as a filtering criterion in your row filter, you are prompted to confirm your decision because we delete row filters that use that table or column.
Use cases
The primary use cases for row filtering are as follows:
- Filtering historical data - For a given table, you can define a filter to sync or exclude rows from a specific time period. For incremental syncs, the filters are applied starting from the next sync after the filters are created.
- Limiting data scope - Since row filters are also applied during incremental syncs, you only sync data that matches the set filtering criteria.
- Syncing or excluding a specific ID value - If your tables are multitenant or you have a specific ID value you explicitly want to or don’t want to sync, you can use filters to select only relevant rows.
- Syncing or excluding records containing a matching string - Similar to filtering by IDs, you can include or exclude rows where a column's string value matches a specified string.
Do not consider row filtering as a way to reduce sync duration. Except for a small number of database connectors, we apply row filtering only after we retrieve the records from the source system. As a result, row filtering generally has no meaningful impact on overall sync duration.
How row filtering works
When you add a filter, we evaluate every sync step against your criteria so that only matching rows continue through the pipeline. Historical operations - such as initial syncs or table re-syncs- respect the filter from the moment the data is queued for processing, ensuring that previously stored records stay aligned with your rules. Incremental syncs honor the same criteria on every run, so any new or updated rows that don’t meet the filter are skipped before they land in your destination.
Some database connectors can push filters down to the source during initial syncs by appending a WHERE clause (or similar constraint) to their queries. Other connectors apply the filter after retrieving the data. Regardless of the connector type, the end result is the same: only the rows that meet your filter conditions are written to your destination.
When you change a filter, we queue a table re-sync so the destination reflects the latest rules. Until that re-sync finishes, the rows that you previously allowed remain in place. Once the re-sync completes, we reconcile any mismatches: in soft delete mode, rows that no longer satisfy the filter are marked as deleted, and if you later broaden the filter, the re-sync repopulates those rows as active records. In history mode, the re-sync closes out the versions that no longer qualify and adds fresh, active versions for the rows that still pass the filter, so you retain a full audit trail while keeping current data aligned with your criteria.
The re-sync also updates the relevant system columns. In soft delete mode, we set _fivetran_deleted to TRUE and refresh the _fivetran_synced timestamp for every row that the new filter excludes; rows that qualify again have _fivetran_deleted reset to FALSE with an updated _fivetran_synced value. In history mode, we flip _fivetran_active to FALSE and populate _fivetran_end for versions that fall out of scope, while rows that stay in scope retain _fivetran_active = TRUE (or receive a new active version) with refreshed _fivetran_synced timestamps and, when a new version is written, an updated _fivetran_start so you can see exactly when the change took effect.
Supported data types
Row filtering is supported for columns with the following data types:
- Integer
- Serial
- Date and Datetime/Timestamp
- String
Supported operators
Row filtering supports the following operators:
- Equal To
- Not Equal To
- Greater Than
- Less Than
- Greater Than Or Equal To
- Less Than Or Equal To
- Is
NULL - Is not
NULL - In (for String, Integer and Serial only)
- Contains (for String only)
- Starts With (for String only)
Ignore trailing spaces
When applied for Strings, the following operators ignore trailing spaces:
- Equal To
- Not Equal To
- Greater Than
- Less Than
- Greater Than Or Equal To
- Less Than Or Equal To
- In
Exception for this rule is the SAP ERP on HANA connector.
Supported connectors
All Fivetran connectors support row filtering.
Limitations
- You can only create up to three conditions per filter.
- You can only create one filter per table.
- You can specify dates for filtering operations on DATE, DATETIME, and TIMESTAMP types only if the year falls within the range 1000 to 9999 (inclusive).
- You can specify integer values for filtering operations on INTEGER and SERIAL types only if they fall within the range -9007199254740991 to 9007199254740991 (inclusive).
- The sync metric Loaded Rows might behave unexpectedly with row filtering. In some cases, filtered out rows will be included in this metric.
- Row filters applied to a parent table are not applied to its child tables.
For connector-specific limitations, see the relevant connector documentation.
Enabling row filter
For existing connections
To create and apply a row filter, do the following:
Open the Schema tab of your Connection Details page.
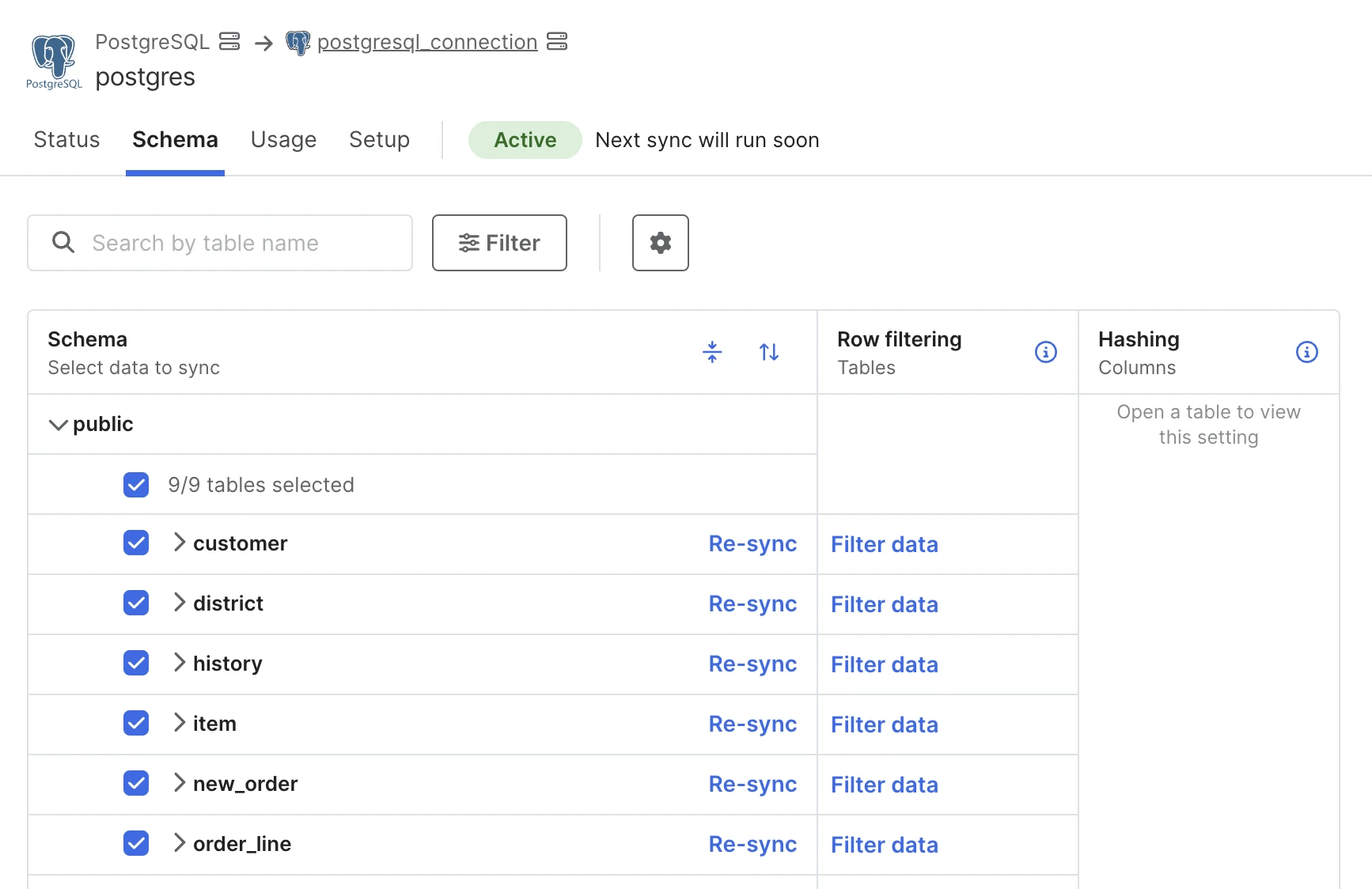
Click Filter Data. The Create a new filter sidebar opens on the right side of the Connection Details page.
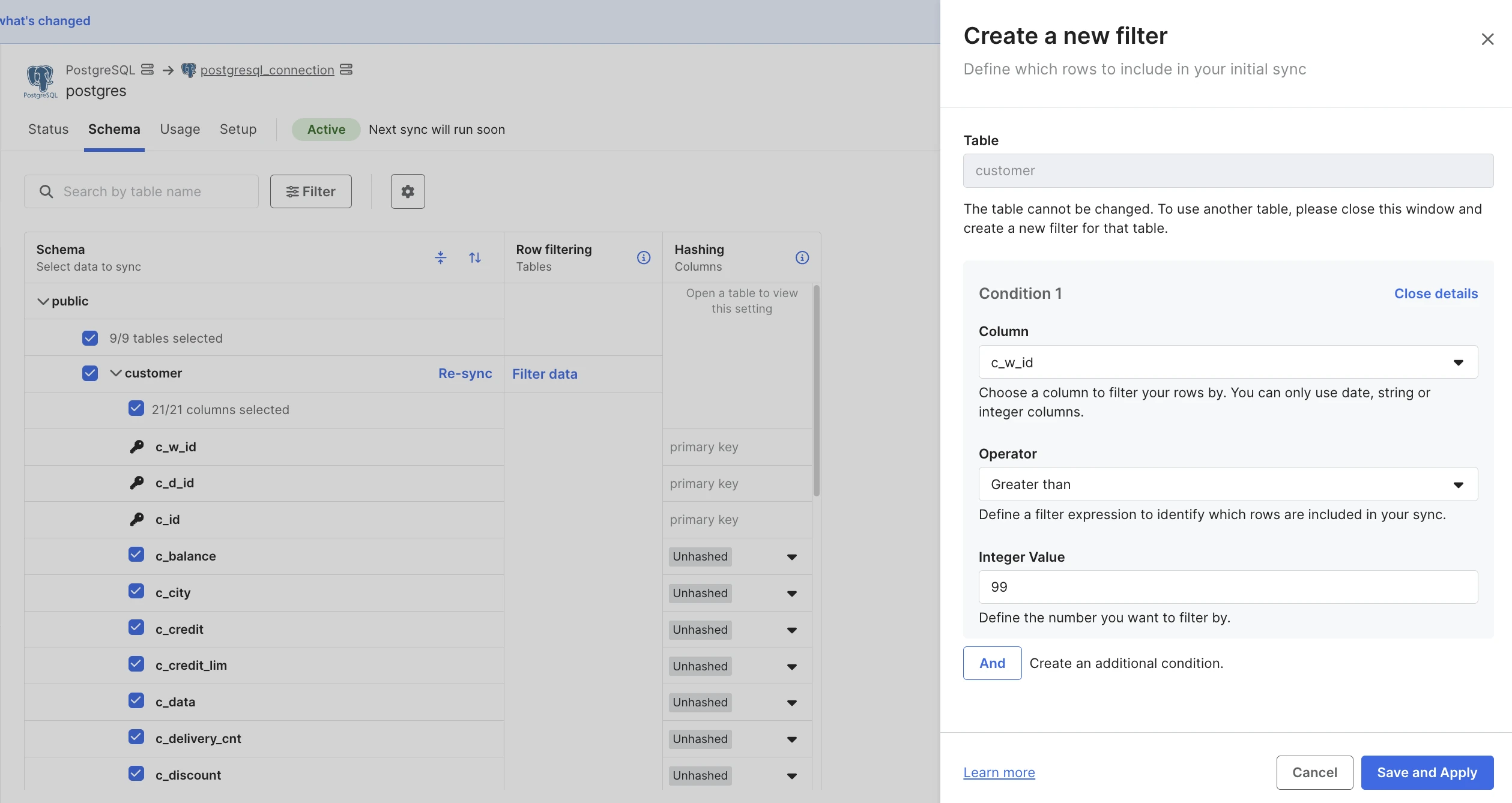
If the table you want to apply the filter to does not have columns of supported types, the message No filterable data will be displayed in the table's row.
Select the Column you want to filter by.
Select the Operator. See the list of supported operators.
Specify the Value as INTEGER, DATE(TIME), or STRING, depending on the column type.
(Optional) Click Add to add another condition. Repeat steps 3 to 5 for each condition.
You can create up to three conditions per filter.
Click Save and Apply. The Apply Row Filter popup opens, notifying you that the table re-sync is required to apply the filter.
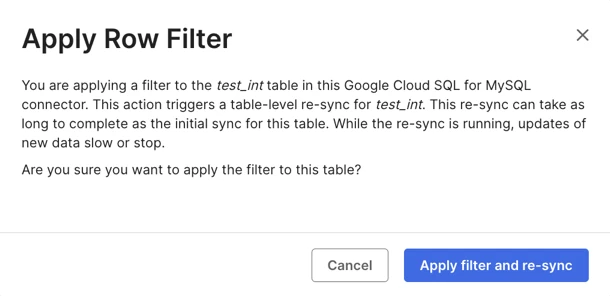
Click Apply filter and re-sync. A table re-sync starts.
A filtered table has a Filtered badge.

For newly created connections
To create and apply a row filter, do the following:
On the Schema tab of the Connector Details page, hover over the table you want to apply the row filter to.
Click Filter Data. The Create a new filter sidebar opens on the right side of the Connection Details page.
If the table you want to apply the filter to does not have columns of supported types, the message No filterable data will be displayed in the table's row.
Select the Column you want to filter by.
Select the Operator. See the list of supported operators.
Specify the Value as integer, date(time), or string depending on the column type.
(Optional) Click Add to add another condition. Repeat steps 3 to 5 for each condition.
You can create up to three conditions per filter.
Click Save and Apply.
Click Save and Continue. You are navigated to the Schema Change Handling Strategy step of the setup guide. The filter is applied during the initial sync.
A filtered table has a Filtered badge.

Editing row filter
To edit a row filter, do the following:
On the Schema tab of the Connection Details page, click Filtered in the relevant table's row. The Filter applied to this table box opens.
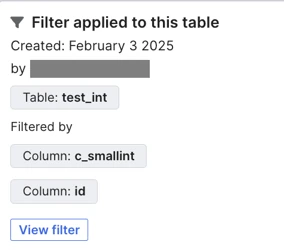
Click View filter. The Edit filter sidebar opens on the right side of the Connection Details page.
You can select to Show details or Close details for each condition.
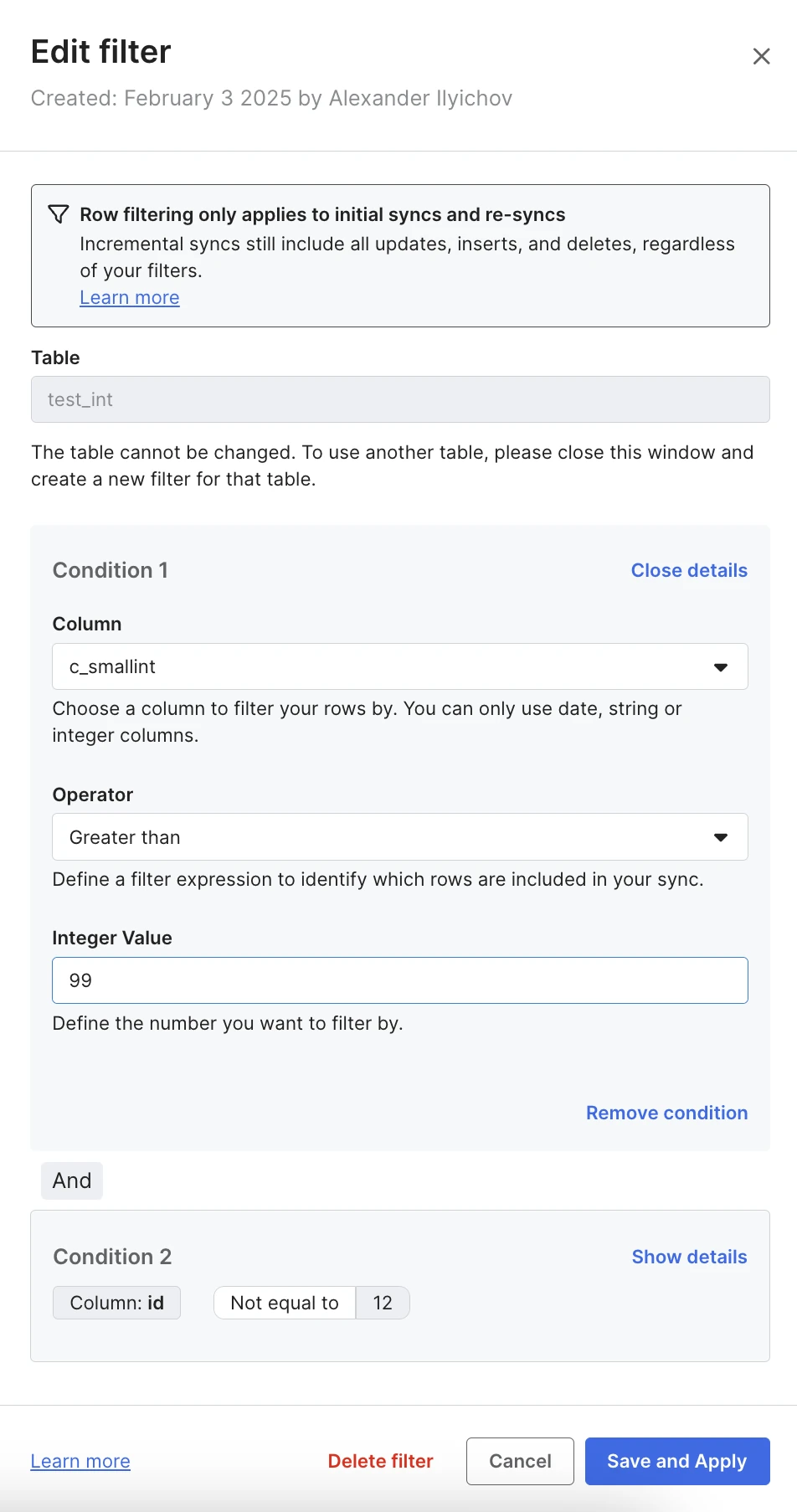
(Optional) You can edit a condition by modifying one or more of the following parameters:
- (Optional) Select the new Column you want to filter by.
- (Optional) Select the new Operator. See the list of supported operators.
- (Optional) Specify the new Value as integer or date, depending on the column type.
(Optional) You can click Add to add another condition. Follow the instructions in the previous step to define the table column, operator, and value for each added condition.
You can create up to three conditions per filter.
(Optional) You can click Remove condition to remove an existing condition.
Click Save and Apply. The Apply Row Filter popup opens, notifying you that the table re-sync is required to apply the filter.

Click Apply filter and re-sync. The table re-sync starts.
Deleting row filter
To delete a row filter, do the following:
On the Schema tab of the Connection Details page, click Filtered in the relevant table's row. The Filter applied to this table box opens.

Click View filter. The Edit filter sidebar opens on the right side of the Connection Details page.

Click Delete filter.
In the Delete data filter and re-sync popup, type DELETE and click Delete filter and re-sync. The table re-sync starts.